Publications
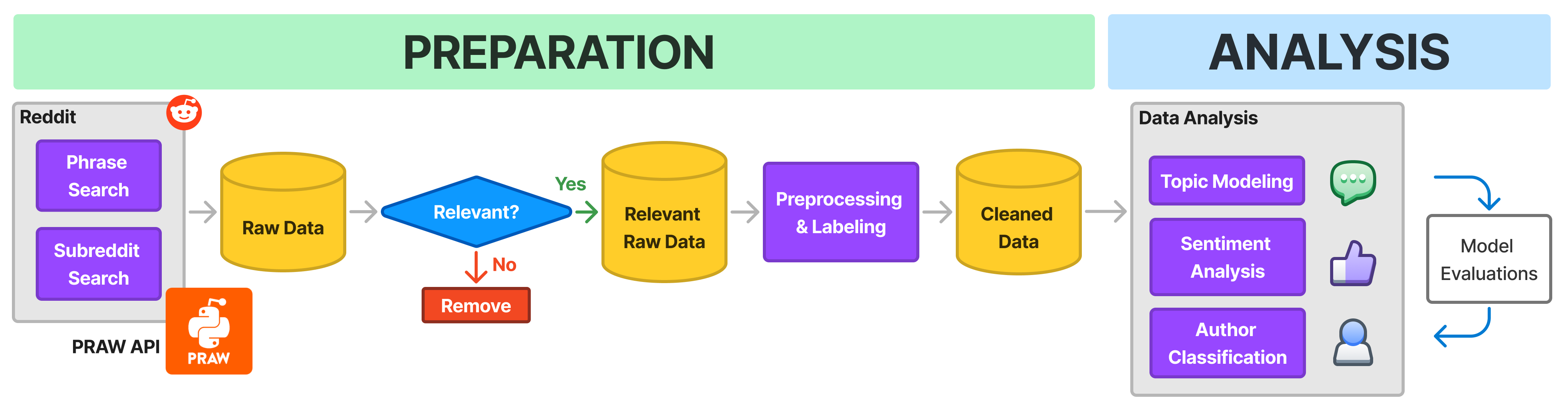
December 18, 2025
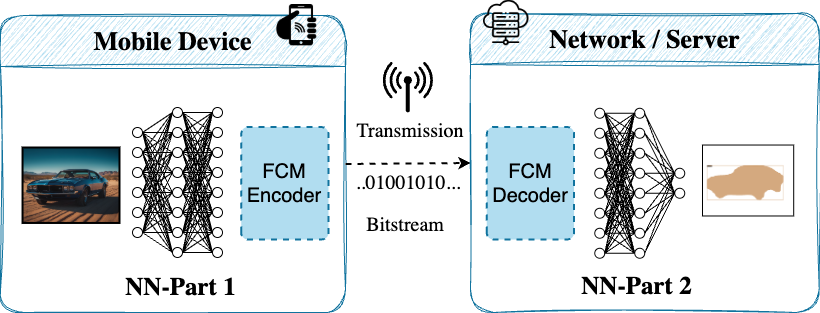
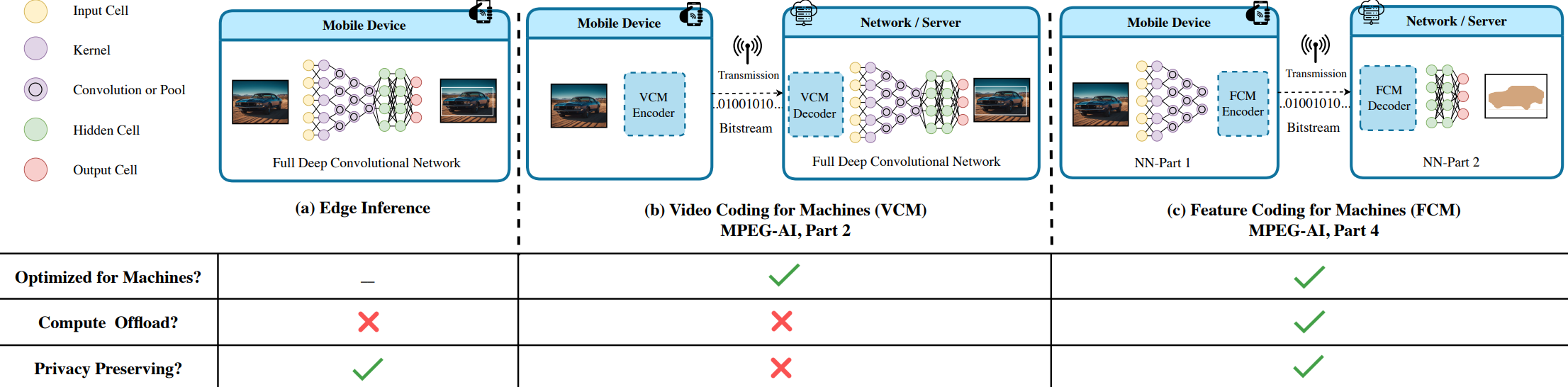
By Paulina DeVito, Akhil Vallala, Sean Mcmahon, Yaroslav Hinda, Benjamin Thaw, Hanqi Zhuang & Hari Kalva
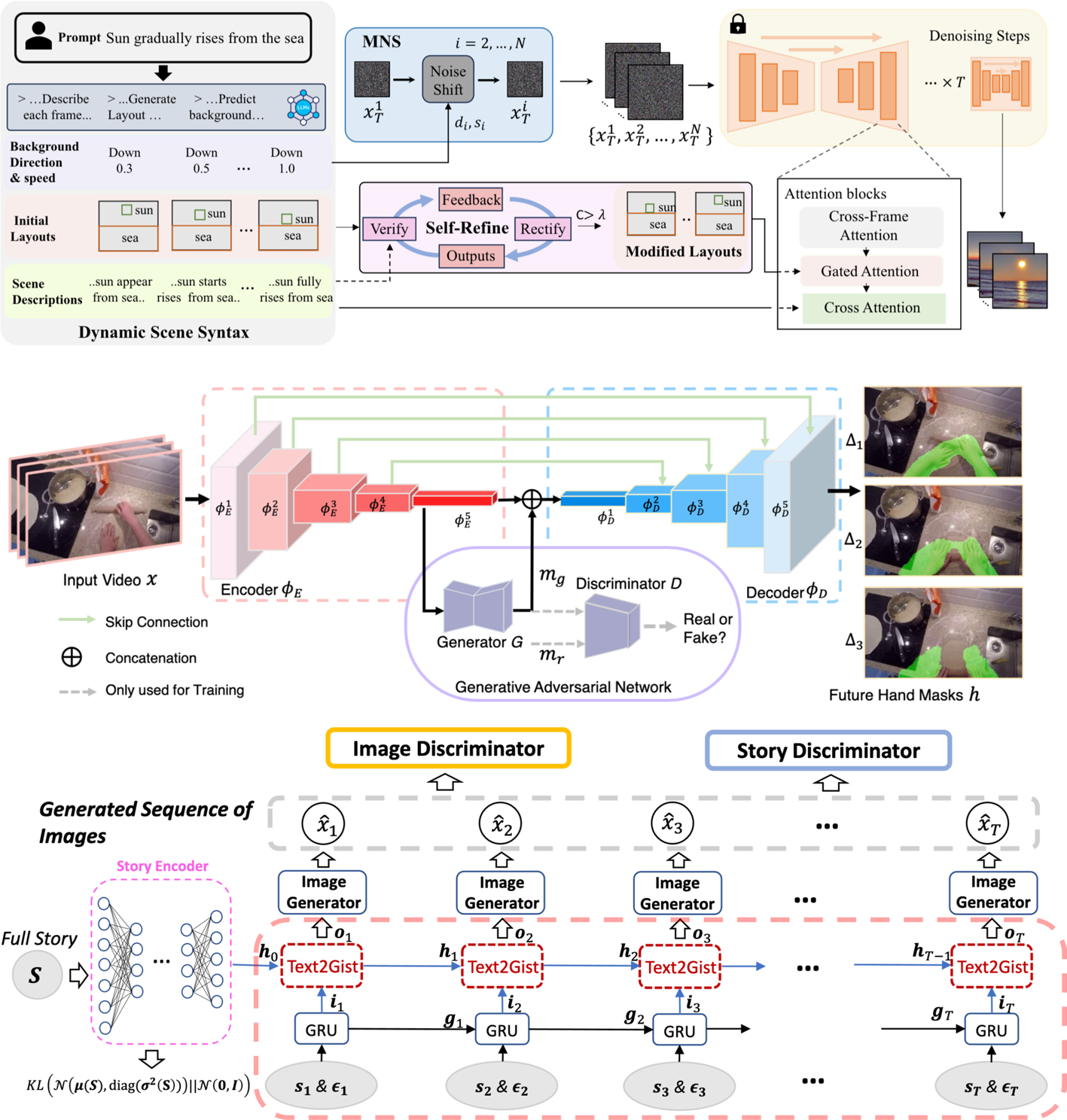
November 14, 2025
By
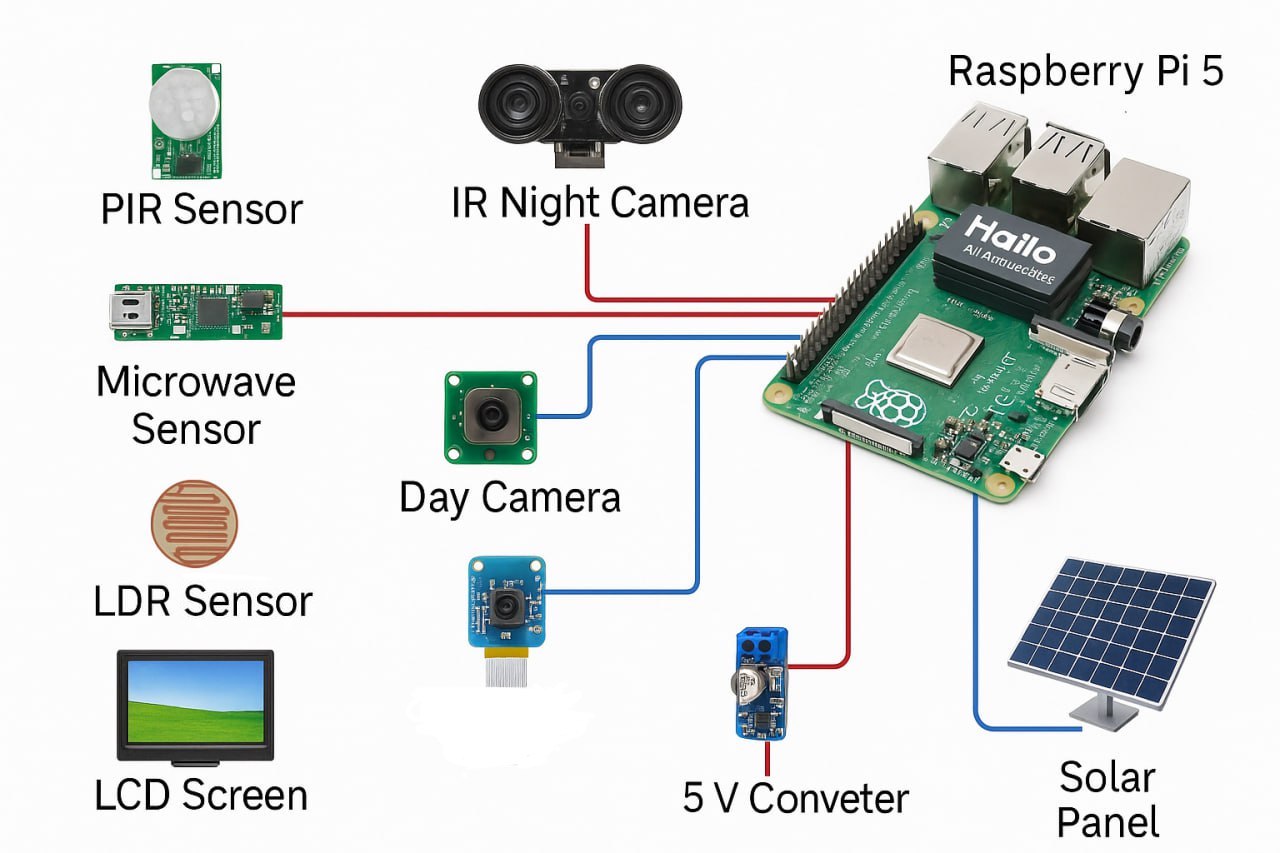
Muhammad Tanveer Jan, Mohammed G. Al-Jassani, Martinraj Nadar, Emmanuel Melchizedek Vunnava, Vangmai Chakrapani, Hayat Ullah, Abbas Khan, Sardar Ali Abbas & Borko Furht
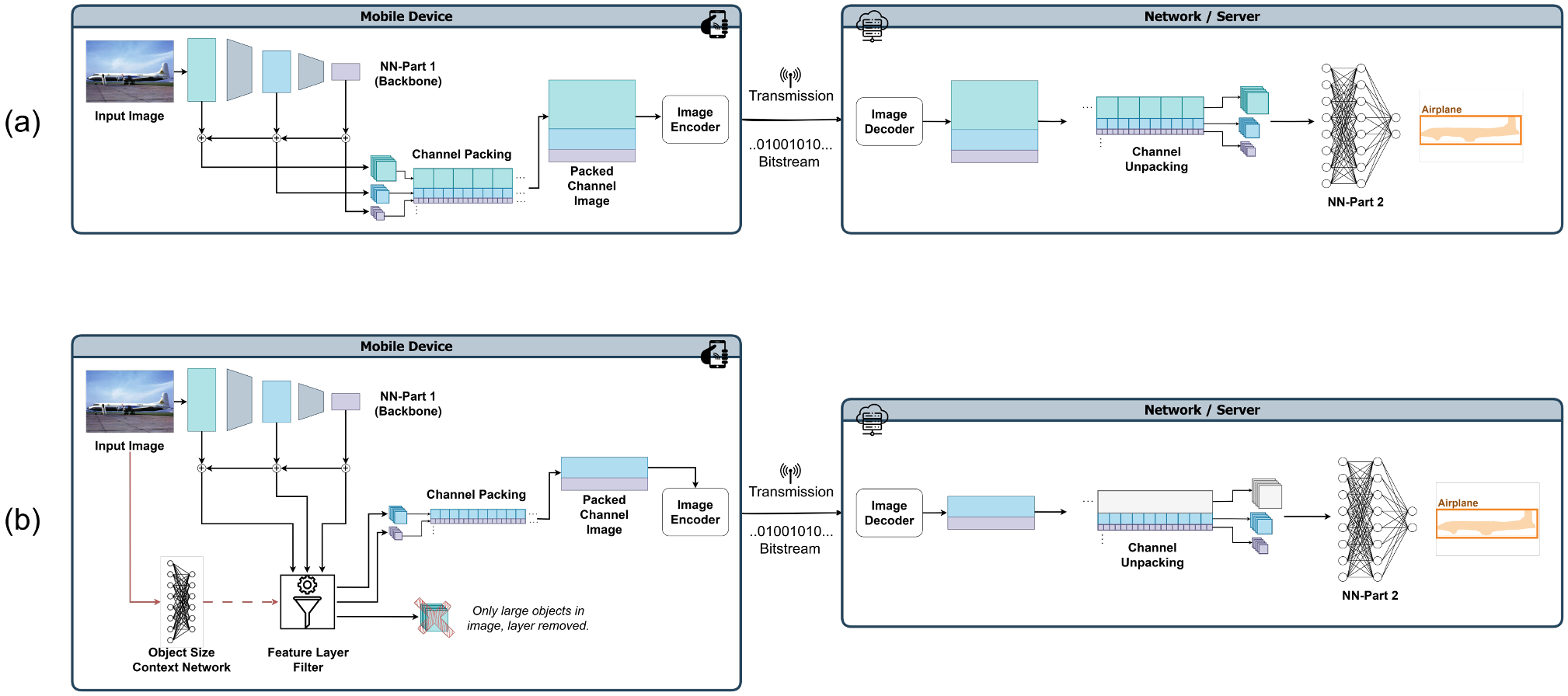
November 11, 2025
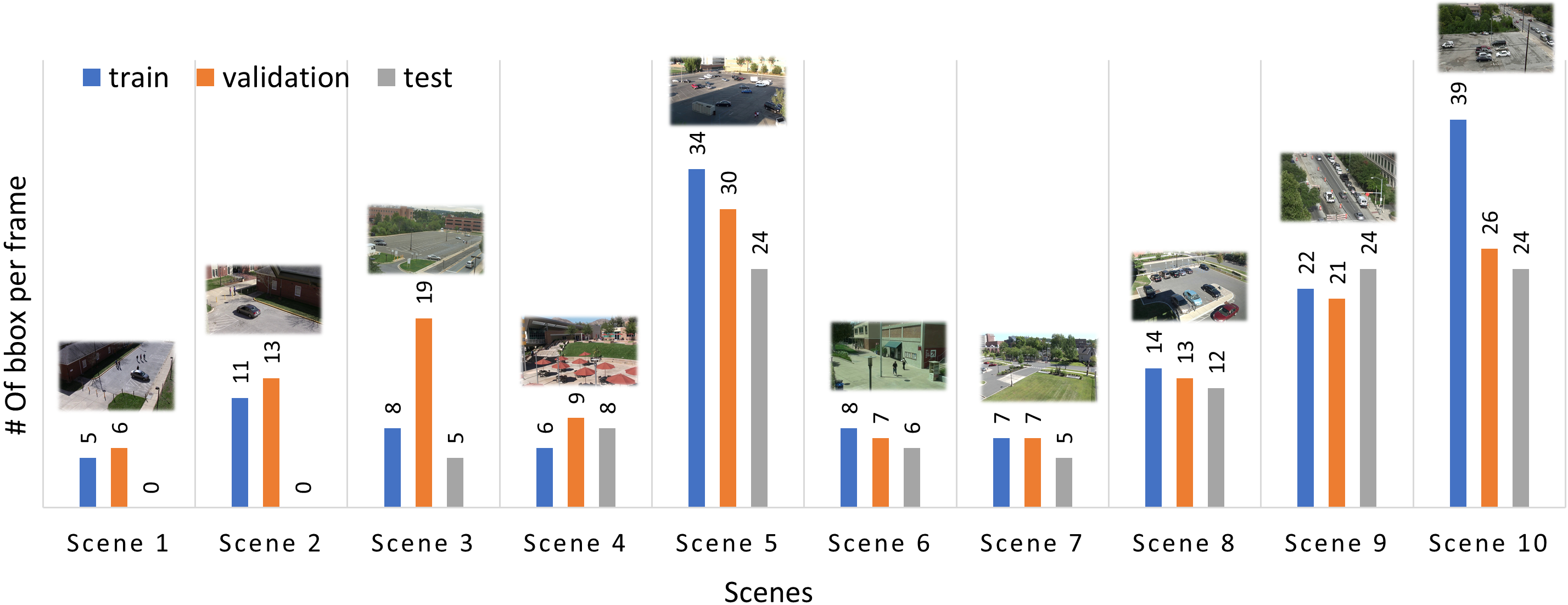
By Juan Merlos, Md Eimran Hossain Eimon, Ashan Perera, Hari Kalva, Velibor Adzic & Borko Furht
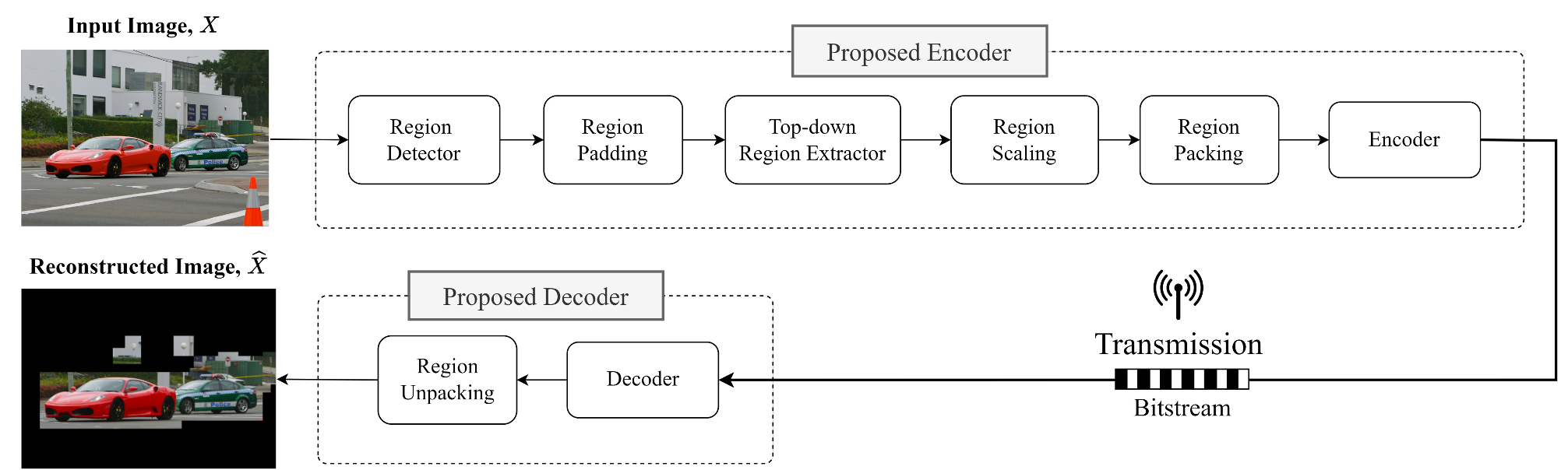
November 11, 2025
By Md Eimran Hossain Eimon, Alena Krause, Ashan Perera, Juan Merlos, Hari Kalva, Velibor Adzic & Borko Furht
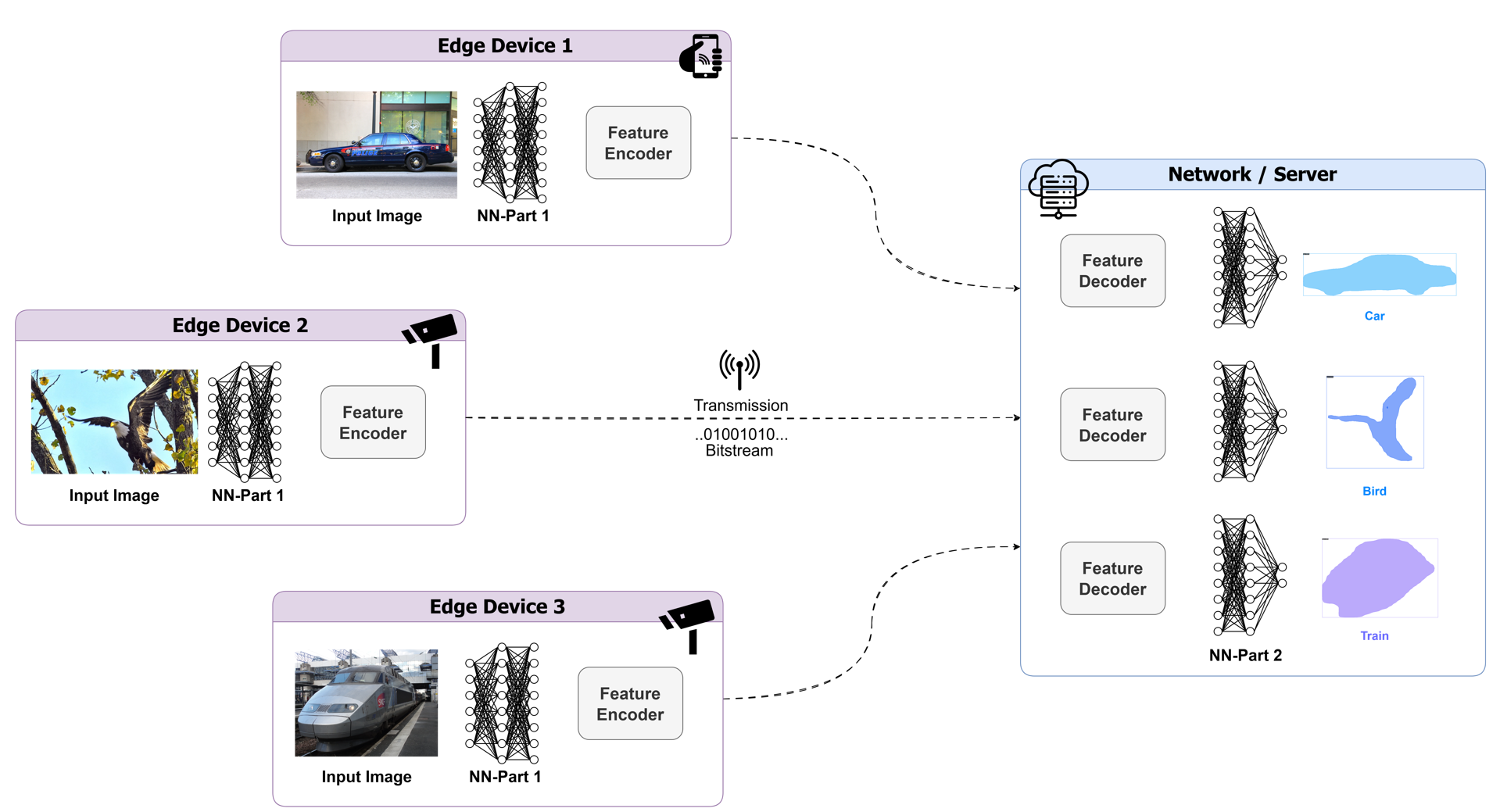
November 07, 2025
By Md Eimran Hossain Eimon, Juan Merlos, Ashan Perera, Hari Kalva, Velibor Adzic & Borko Furht
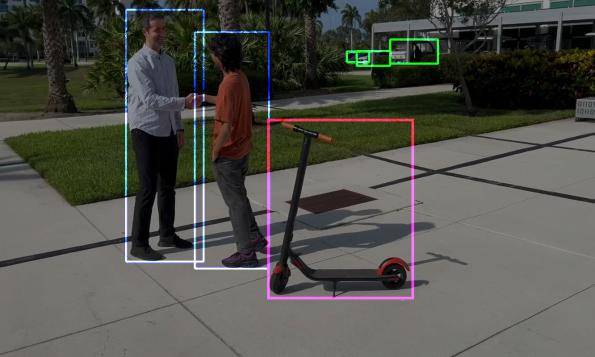
October 27, 2025
By Ashan Perera, Md Eimran Hossain Eimon, Juan Merlos, Velibor Adzic, Hari Kalva & Borko Furht