Data Embedding in Digital Media
Slide-1
Optimal Spread-Spectrum and Least-Significant-Bit Methods
Connor Weeks
Email: crweeks@knox.edu

Slide-2
Project Summary
- Steganography
- Digital Steganography
- Least-Significant Bit Method
- Optimal Spread Spectrum Method
Slide-3
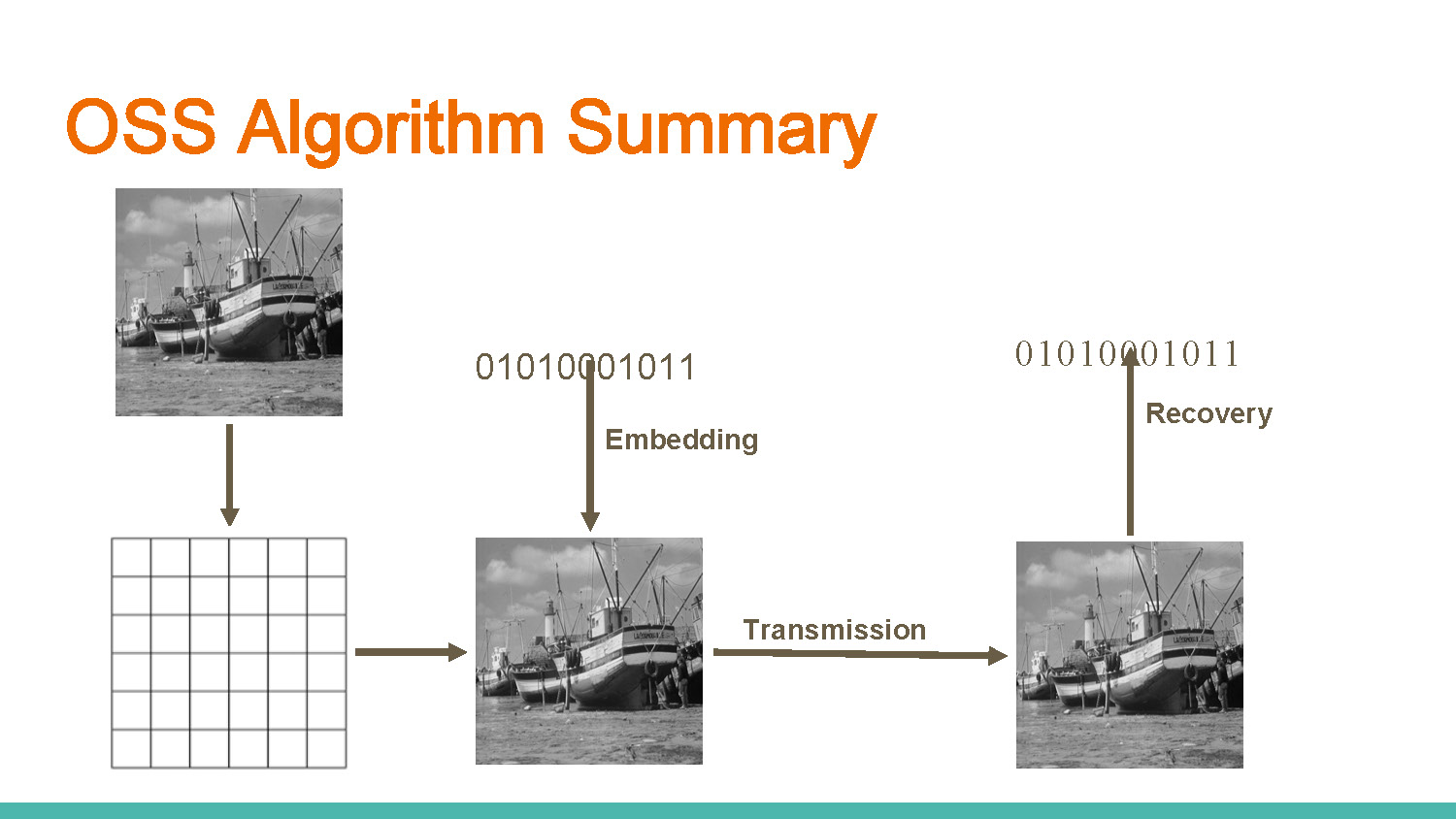
OSS Algorithm Summary
Process flow showing binary data 01010001011 going through three stages:
- Transmission
- Embedding
- Recovery
Slide-4
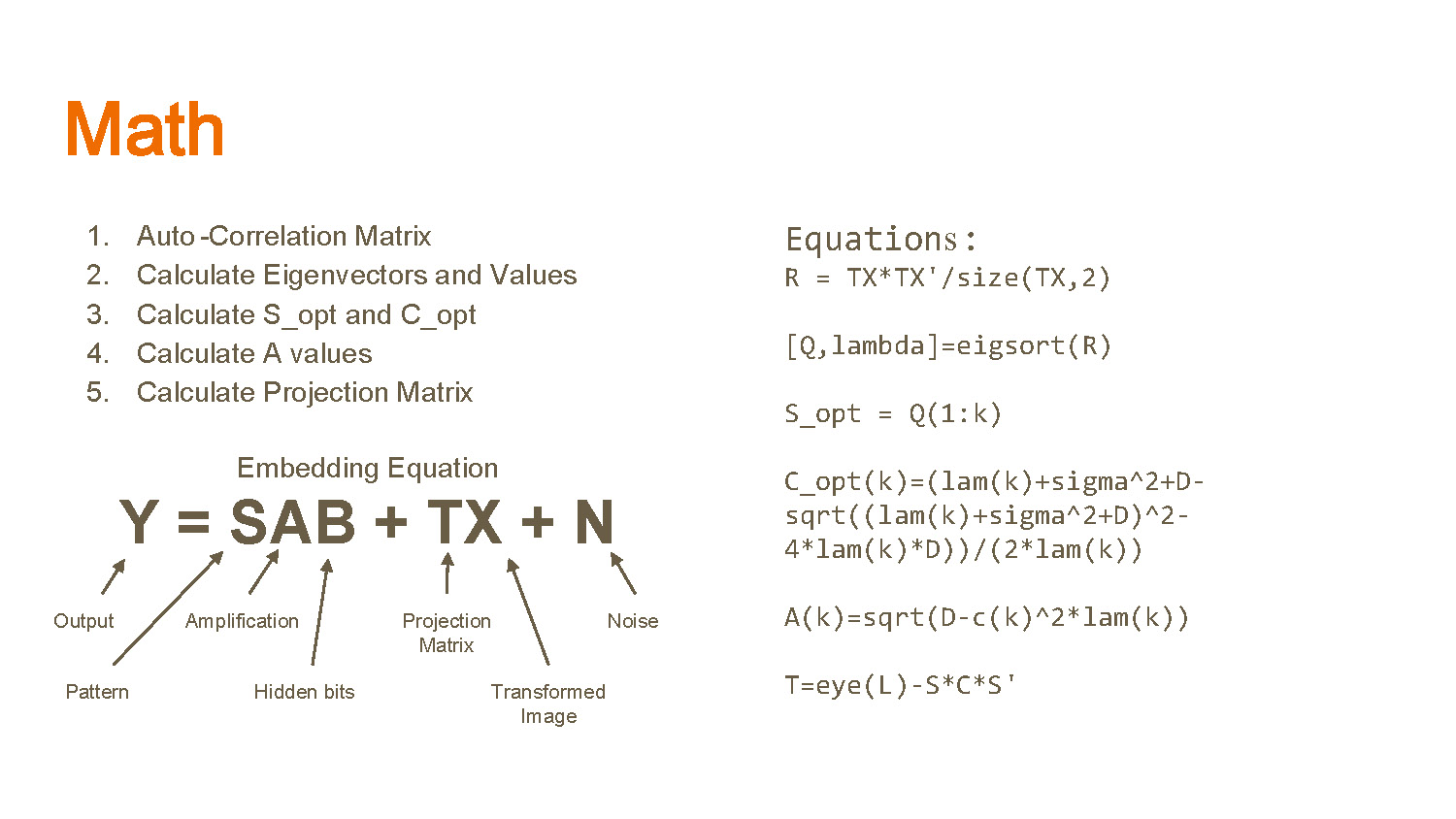
Math
- Auto-Correlation Matrix
- Calculate Eigenvectors and Values
- Calculate S_opt and C_opt
- Calculate A values
- Calculate Projection Matrix
Embedding Equation
Y = SAB + TX + N
- Output Pattern
- Amplification
- Hidden bits
- Projection Matrix
- Transformed Image
- Noise
Equations:
R = TX*TX'/size(TX,2)
[Q,lambda]=eigsort(R)
S_opt = Q(1:k)
C_opt(k)=(lam(k)+sigma^2+D-sqrt((lam(k)+sigma^2+D)^2-4*lam(k)*D))/(2*lam(k))
A(k)=sqrt(D-c(k)^2*lam(k))
T=eye(L)-S*C*S'

Slide-5
Comparison
Optimal Spread Spectrum
- Works with lossy compression
- Harder to detect with steganalysis
- Works with additive noise
Least Significant Bit Replacement
- No bit errors (lossless compression)
- 4-12 times more storage
- No recovery key
- Computationally faster
- Less distortion

Slide-6
References
M. Gkizeli, D. A. Pados, and M. J. Medley, "Optimal signature design for spread-spectrum steganography," IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 16, pp. 391-405, Feb. 2007.
Ming Li, Ngwe Thawdar, Dimitris A. Pados, Stella N. Batalama, and Michael J. Medley, "Minimum-Distortion Data Embedding in Video Streams" IEEE ICC 2014.

End of Presentation
Click the right arrow to return to the beginning of the slide show.
For a downloadable version of this presentation, email: I-SENSE@FAU.