POWERGPT

Slide-1
Faculty Mentor: Yufei Tang, Ph.D.
Student Mentor: Raul Mendy
Rithika Mathew, Siyuan Du
Slide-2
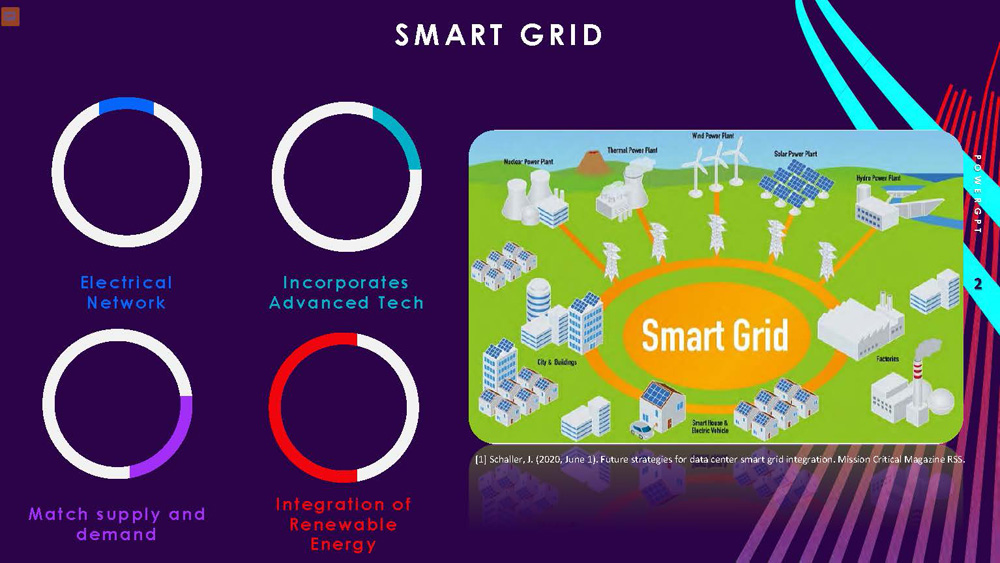
SMART GRID POWERGPT
Electrical Network
Match supply and demand
Integration of Renewable Energy
Incorporates Advanced Tech
[1] Schaller, J. (2020, June 1). Future strategies for data center smart grid integration. Mission Critical Magazine RSS.
Slide-3
BACKGROUND POWERGPT
Integration of new technologies into the electrical grid has a multitude of benefits, but also creates diverse strains on the system
Smart grids need more advanced maintenance and management techniques
Existing strategies:
Scheduled - Periodic deployment of teams to oversee machines and perform maintenance
Reactive - Relies on highly accurate sensing equipment, Prolonged service delays
Slide-4
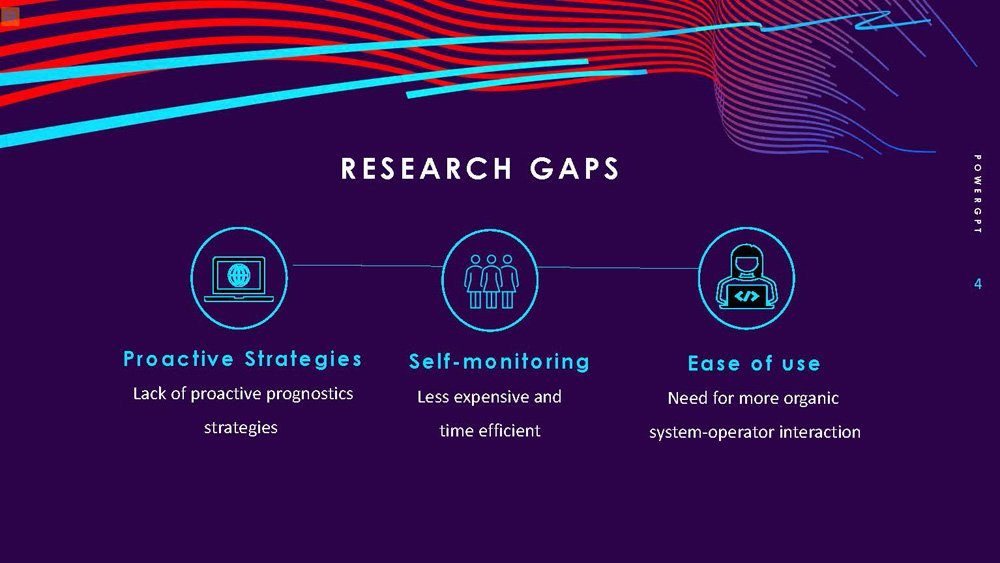
RESEARCH GAPS POWERGPT
Proactive Strategies: Lack of proactive prognostics strategies
Self-monitoring: Less expensive and time efficient
Ease of use: Need for more organic system-operator interaction

Slide-5
PROPOSED SOLUTION - POWERGPT
Large Scope: National grid map and wind power prediction
Dynamic Visuals: Transformer graphics, map, and diagrams
Predictive: Transformer based fault detection
UI: Tkinter to React based
History: PostgreSQL storage
Session Management: Login Page

Slide-6
FEATURES POWERGPT
Login: User authentication
History: Chat retrieval
Interactive Features: Graph & diagram
Wind Power: Live generation predictions
Power Grid: Color-coded plants

Slide-7
LOGIN / CHAT HISTORY POWERGPT
User Query history
Automatically logs to PostgreSQL database for retrieval
Login page for session management
Information stored on database
Password login planned for future implementation
Features such as chat history will be per-user based
Slide-8
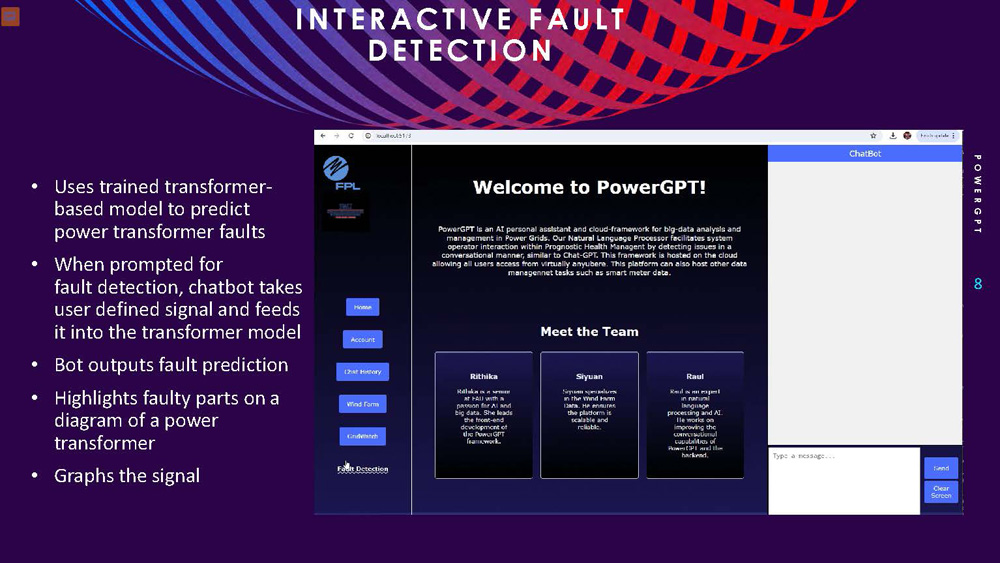
INTERACTIVE FAULT DETECTION POWERGPT
Uses trained transformer-based model to predict power transformer faults
When prompted for fault detection, chatbot takes user defined signal and feeds it into the transformer model
Bot outputs fault prediction
Highlights faulty parts on a diagram of a power transformer
Graphs the signal
Slide-9
GRIDWATCH POWERGPT
This slide displays a world map visualization showing global power grid monitoring capabilities, with various power generation facilities and grid connections represented across different continents.
Slide-10
WIND POWER POWERGPT
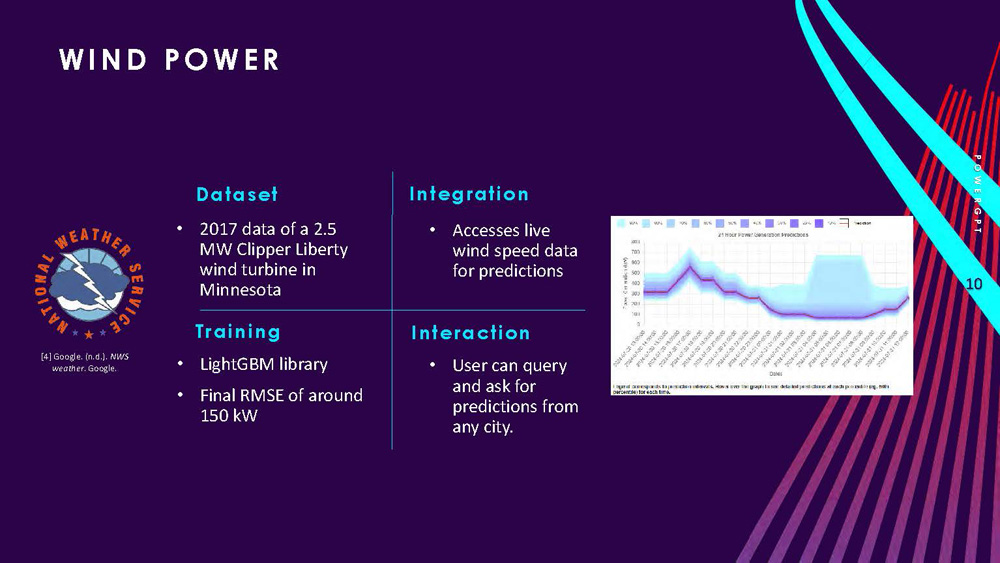
Dataset: 2017 data of a 2.5 MW Clipper Liberty wind turbine in Minnesota
Training: LightGBM library, Final RMSE of around 150 kW
Integration: Accesses live wind speed data for predictions
Interaction: User can query and ask for predictions from any city.
Slide-11
WIND POWER POWERGPT
This slide shows a screenshot of the wind power prediction interface, displaying real-time wind power generation predictions with numerical data and interactive elements for user queries and results visualization.

Slide-12
CHATBOT POWERGPT
Makes interaction with the system organic and conversational
Prompt-based interaction with various features.
React and Flask Framework for connecting frontend and backend
Slide-13
FUTURE WORKS POWERGPT
Security: Implement secure password protection for user accounts.
Enhanced Chatbot: Improve the chatbot's responsiveness to match the capabilities of ChatGPT.
Chat History: Include diagram and graph
Wind Prediction: Change to transformer model – better long-term dependencies

Slide-14
REFERENCES POWERGPT
- Schaller, J. (2020, June 1). Future strategies for data center smart grid integration. Mission Critical Magazine RSS. https://www.missioncriticalmagazine.com/articles/93008-future-strategies-for-data-center-smart-grid-integration
- Accurso, J., Mendy, R., Torres, A., & Tang, Y. (2023). A ChatGPT-like solution for power transformer condition monitoring. In 2023 International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA) (pp. 1716-1722). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMLA58977.2023.00260
- Asimislam. (2022, November 20). Global Power Generation - Eda & World Map. Kaggle. https://www.kaggle.com/code/asimislam/global-power-generation-eda-world-map
- Google. (n.d.). NWS weather - apps on Google Play. Google. https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.daugherty.nws_remastered&hl=en_US
- Davison, Brian. (2019). Rich Data for Wind Turbine Power Performance Analysis. Retrieved from the Data Repository for the University of Minnesota (DRUM), https://doi.org/10.13020/1etn-1q17.

Slide-15
THANK YOU! POWERGPT
Acknowledgement: This work was supported in part by the U.S. National Science Foundation under Grant Nos. CNS-1950400 (I-SENSE REU SITE) & CMMI-2145571 (CAREER Award) and the FPL Intelligent Energy Technologies (InETech) Center Summer Internship Program at FAU.

End of Presentation
Click the right arrow to return to the beginning of the slide show.
For a downloadable version of this presentation, email: I-SENSE@FAU.