Advance AI-Driven Urban Safety Systems for Smart Cities using YOLO9

Slide-1
REU Scholar: Briana Deloatch
REU Mentor: Dr. Yufei Tang
Home Institute: Lehman College, City University of New York (CUNY)

Slide-2
Motivation
There are many discussions about creating safety within urban cities. With the development of AI, this idea can be achieved sooner than many may believe.
Streetscapes (CS3) aims to modernize what improved safety in urban communities may look like with the development of AI.
This project will use a SOTA machine learning algorithm and 3D LiDAR data to estimate the social distance, thus enhancing urban designs and safety.
Slide-3
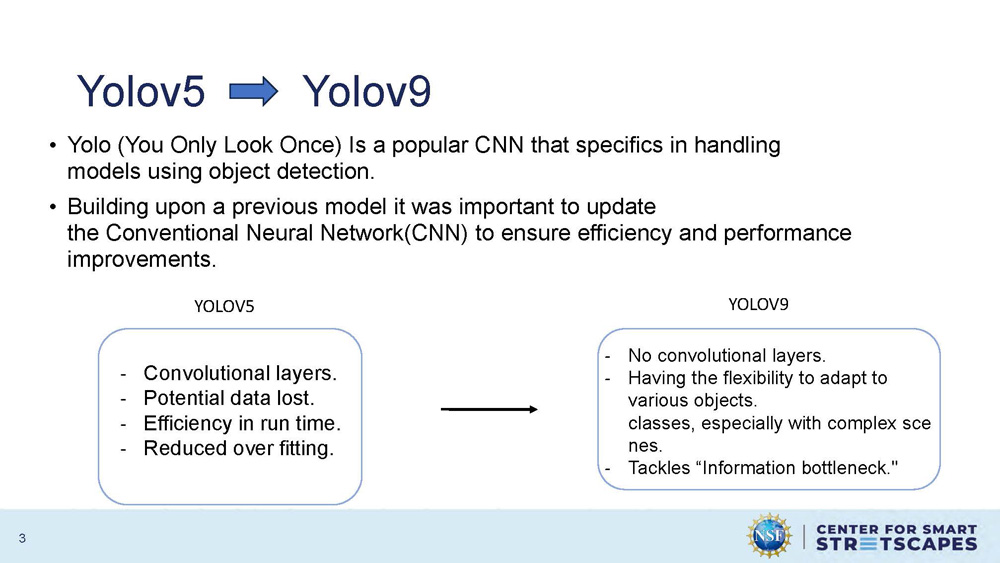
Yolov5 Yolov9
Yolo (You Only Look Once) Is a popular CNN that specifics in handling models using object detection.
Building upon a previous model it was important to update the Conventional Neural Network(CNN) to ensure efficiency and performance improvements.
| YOLOV5 | YOLOV9 |
|---|---|
| Convolutional layers. | No convolutional layers. |
| Potential data lost. | Having the flexibility to adapt to various objects classes, especially with complex scenes. |
| Efficiency in run time. | Tackles "Information bottleneck." |
| Reduced over fitting. |

Slide-4
Research Goals
• Generalizability: create a robust model that can detect many different scenarios.
• Training Efficiency: propose an approach to augment image data for training.
• Testing Accuracy: obtain the best ratio of different classes.

Slide-5
Data Utilized
Utilizing the existing social distancing(Ouster LiDAR) dataset and enhancing the model by incorporating additional dataset (Velodyne LiDAR) to replicate an urban city environment.
Roboflow, a computer vision tool to help classify objects.
The Codebase Google Colab creates an ease application process for training data.
Two LiDAR datasets are shown: Velodyne LiDAR and Ouster LiDAR with sample point cloud visualizations of urban environments. A red video placeholder is on the bottom right of the slide.
Slide-6
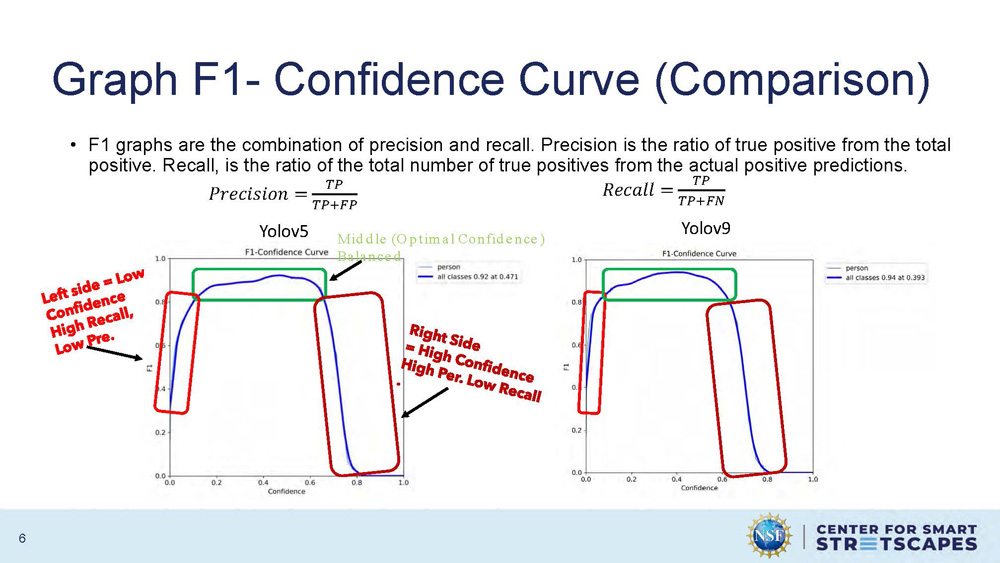
Graph F1- Confidence Curve (Comparison)
F1 graphs are the combination of precision and recall. Precision is the ratio of true positive from the total positive. Recall, is the ratio of the total number of true positives from the actual positive predictions.
Mathematical formulas:
Precision = TP/(TP+FP)
Recall = TP/(TP+FN)
The graph shows F1-Confidence curves for both Yolov5 and Yolov9, with Yolov5 showing "Middle (Optimal Confidence)" and "Balanced" performance characteristics. The curves demonstrate the relationship between confidence levels and F1 scores for model performance evaluation.
Slide-7
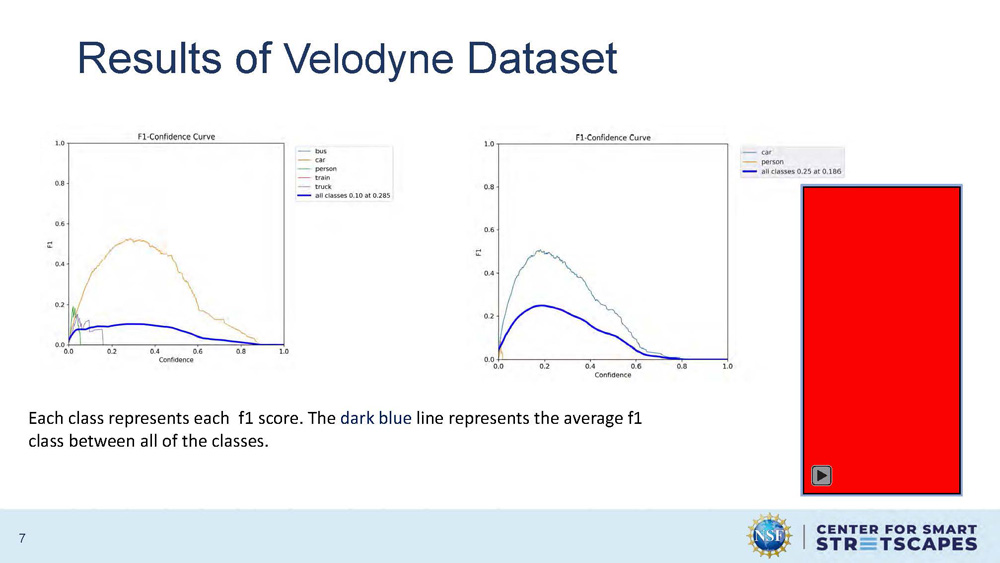
Results of Velodyne Dataset
Each class represents each f1 score. The dark blue line represents the average f1 class between all of the classes.
The graph displays F1 scores across different object detection classes, with individual class performance shown and an average performance line highlighted in dark blue. The results demonstrate the model's ability to detect various objects in the Velodyne LiDAR dataset.
Slide-8
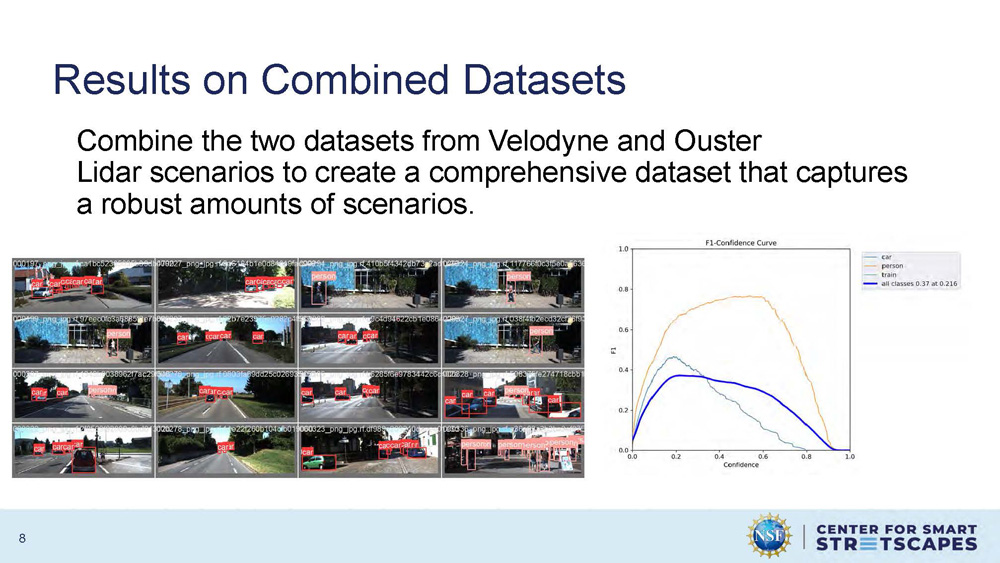
Results on Combined Datasets
Combine the two datasets from Velodyne and Ouster Lidar scenarios to create a comprehensive dataset that captures a robust amounts of scenarios.
The slide presents the results of combining both LiDAR datasets to create a more comprehensive training dataset that better represents diverse urban environments and scenarios.

Slide-9
Conclusion
Adopted Yolov9 for better model performance (accuracy and computational complexity).
Used the previous dataset from the social distancing project and incorporated a new dataset to replicate the urban environment for object detection was successful.
This project brings us one step closer to documenting urban safety and continuing the goal of CS3.

Slide-10
References
• Kaur, R., & Singh, S. (2023). A comprehensive review of object detection with deep learning. Digital Signal Processing, 132, 103812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsp.2022.103812
• A Federated Learning-Based License Plate Recognition Scheme for 5G-Enabled internet of vehicles. (2021, December 1). IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=9381655&tag=1
• He, K. H., Zhang, X. Z., Ren, S. R., & Sun, J. S. (2015). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Arxiv (arXiv:1512.03385v1). Arxiv. Retrieved December 10, 2015, from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385
• Szegedy, C., Toshev, A., Erhan, D., & Google, Inc. (n.d.). Deep neural networks for object detection. In Google, Inc. [Journal-article]. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2013/file/f7cade80b7cc92b991cf4d2806d6bd78-Paper.pdf
• Gkioxari, G., Girshick, R., Doll´Ar, P., He, K., & Facebook AI Research (FAIR). (n.d.). Detecting and recognizing Human-Object interactions. Facebook AI Research (FAIR). https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/papers_backup/Gkioxari_Detecting_and_Recognizing_CVPR_2018_paper.pdf

Slide-11
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation (EEC- 2133516).

Slide-12
Thank You
LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/briana-deloatch
GitHub: brianad459 (github.com)

End of Presentation
Click the right arrow to return to the beginning of the slide show.
For a downloadable version of this presentation, email: I-SENSE@FAU.