Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3

Slide-1
Memory, Throughput, and Security Software Optimizations on ARMv7m Cortex-M4
REU Scholar: Maggie Simmons
REU Mentor: Dr. Reza
Home University: Rice University
August 1, 2024
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 1 / 14

Slide-2
IoT Device Security
Challenges with IoT Security
- IoT Devices → low computational resources
- Side-Channel Attacks: extract secrets through inadvertently leaked information
- Hardware solutions to cryptographic problems can be expensive
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 2 / 14
Slide-3
Quantum Age: Coming Soon
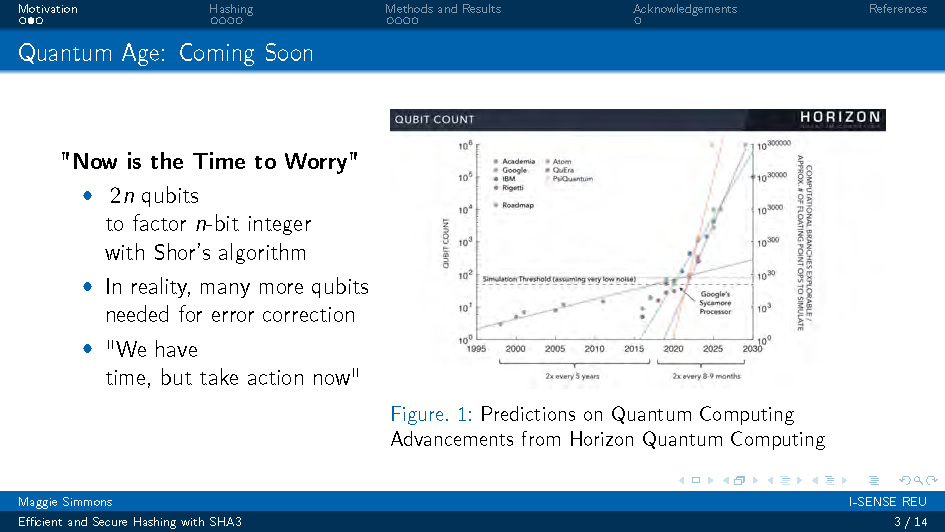
Figure. 1: Predictions on Quantum Computing Advancements from Horizon Quantum Computing
"Now is the Time to Worry"
- 2n qubits to factor n-bit integer with Shor's algorithm
- In reality, many more qubits needed for error correction
- "We have time, but take action now"
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 3 / 14
Slide-4
What is Post Quantum Cryptography?
Objective
- Secure systems against both quantum and classical computers, without changing existing communications protocols
Structure
- Cryptographic algorithms built from common set of building blocks called "primitives"
Right: https://quantumai.google/discover/whatisqc
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 4 / 14
Slide-5
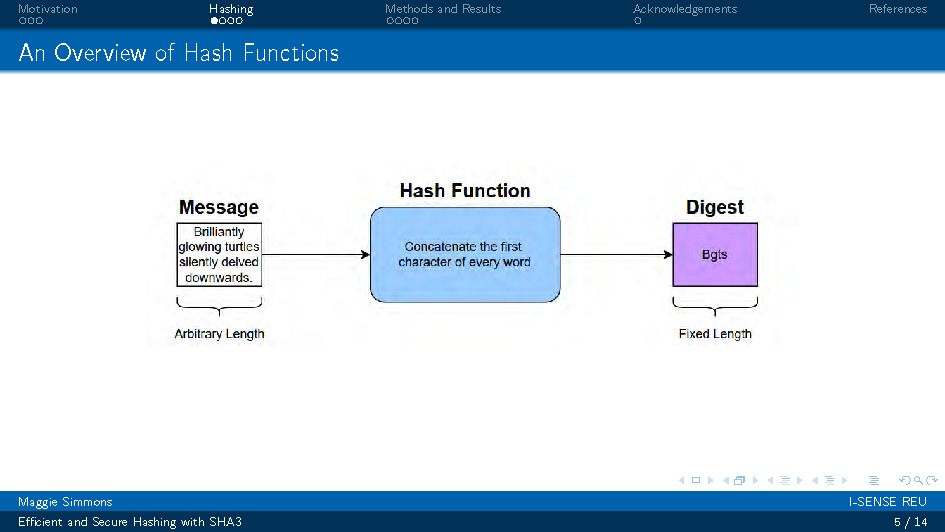
An Overview of Hash Functions
This slide contains a diagram showing the basic concept of hash functions. The diagram illustrates how hash functions take input data of any size and produce a fixed-size output hash value. The visual shows the flow from input through the hash function to produce the digest output.
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 5 / 14
Slide-6
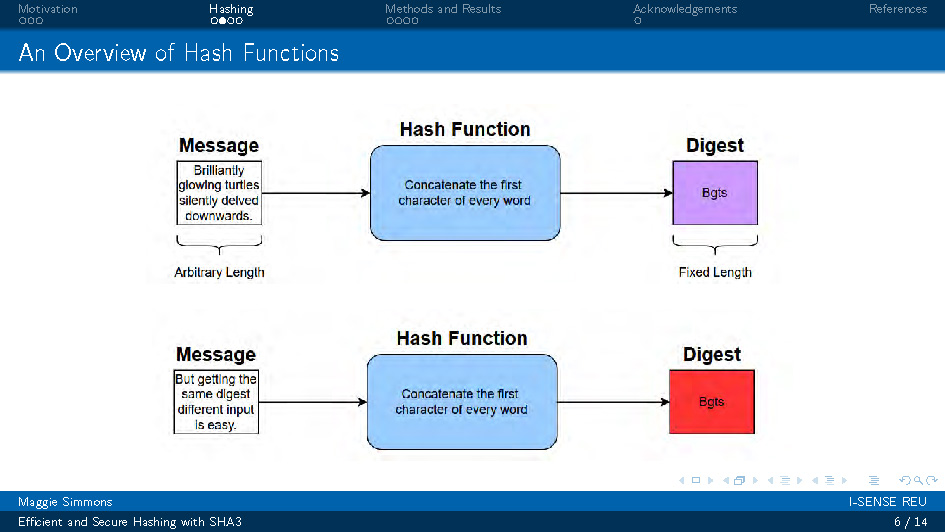
An Overview of Hash Functions
This slide continues the overview of hash functions, showing additional properties and characteristics of cryptographic hash functions. The content builds upon the previous slide to provide more comprehensive understanding of hash function behavior and requirements.
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 6 / 14
Slide-7
SHA3 Overview
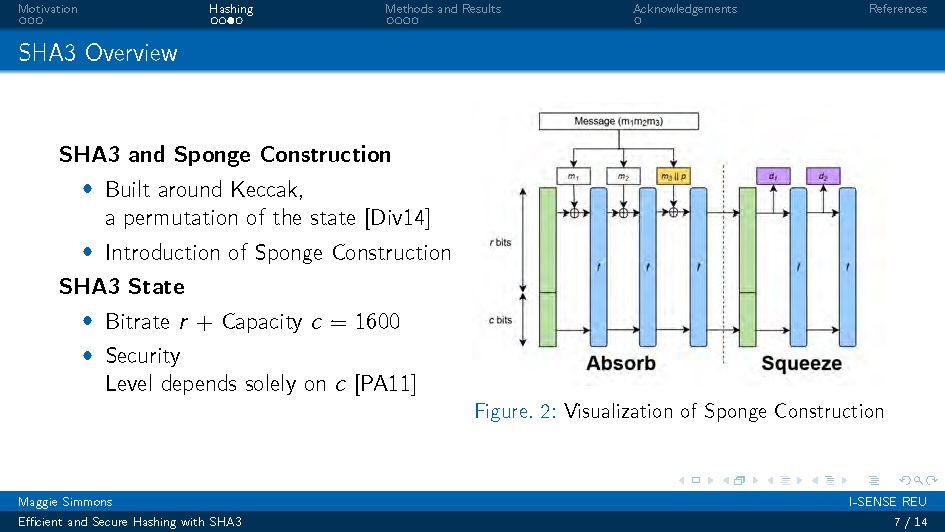
Figure. 2: Visualization of Sponge Construction
SHA3 and Sponge Construction
- Built around Keccak, a permutation of the state [Div14]
- Introduction of Sponge Construction
SHA3 State
- Bitrate r + Capacity c = 1600
- Security Level depends solely on c [PA11]
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 7 / 14
Slide-8
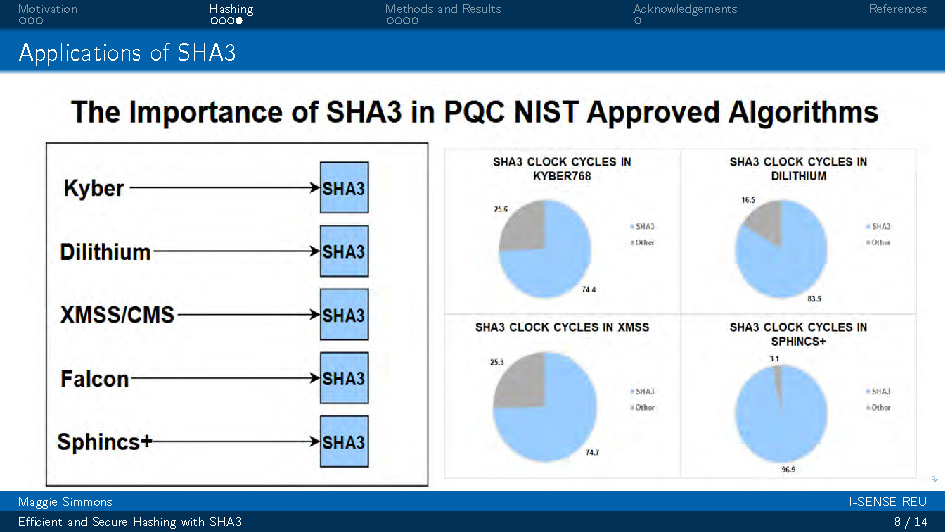
Applications of SHA3
This slide presents various applications and use cases of SHA3 hashing algorithm. The content shows how SHA3 is implemented across different systems and contexts, demonstrating its versatility and importance in modern cryptographic applications.
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 8 / 14
Slide-9
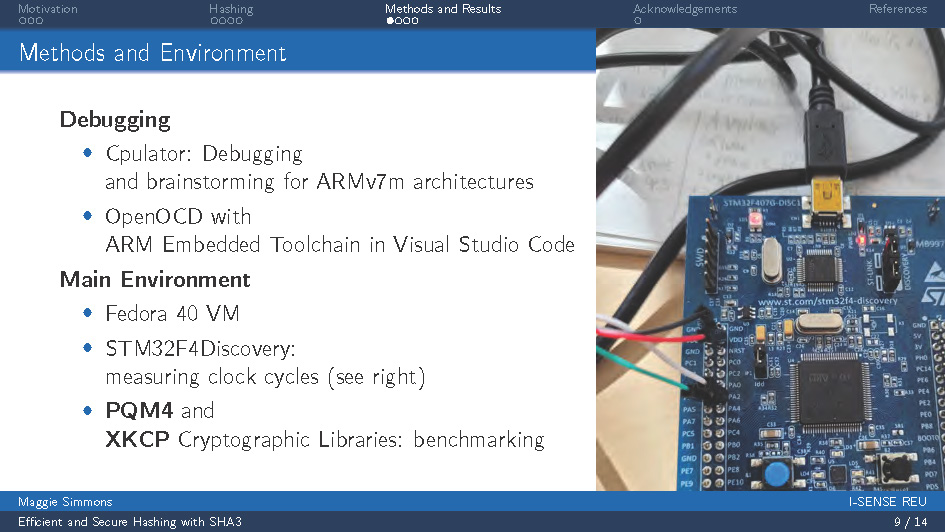
Methods and Environment
Debugging
- Cpulator: Debugging and brainstorming for ARMv7m architectures
- OpenOCD with ARM Embedded Toolchain in Visual Studio Code
Main Environment
- Fedora 40 VM
- STM32F4Discovery: measuring clock cycles (see right)
- PQM4 and XKCP Cryptographic Libraries: benchmarking
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 9 / 14
Slide-10
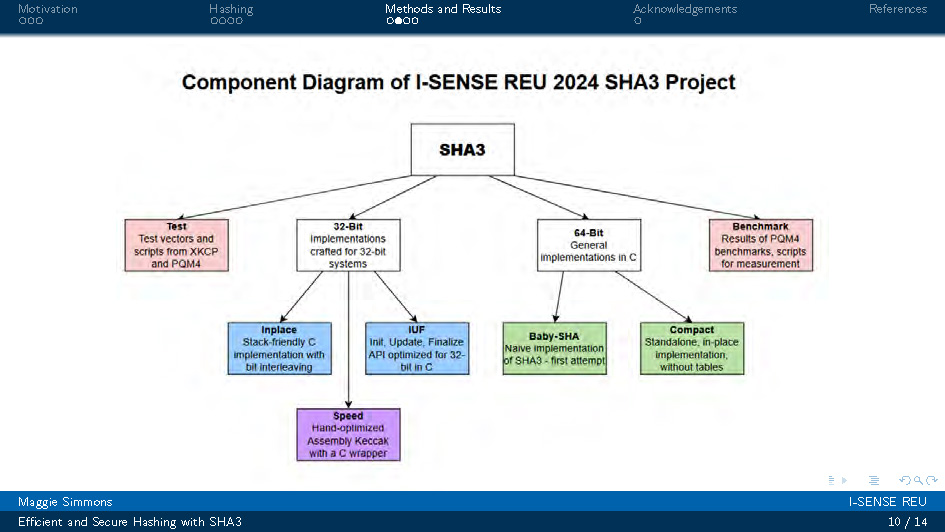
This slide presents results and performance data from the testing and benchmarking conducted during the research. The content includes performance metrics and analysis of the SHA3 implementation optimizations on the ARMv7m Cortex-M4 architecture.
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 10 / 14
Slide-11
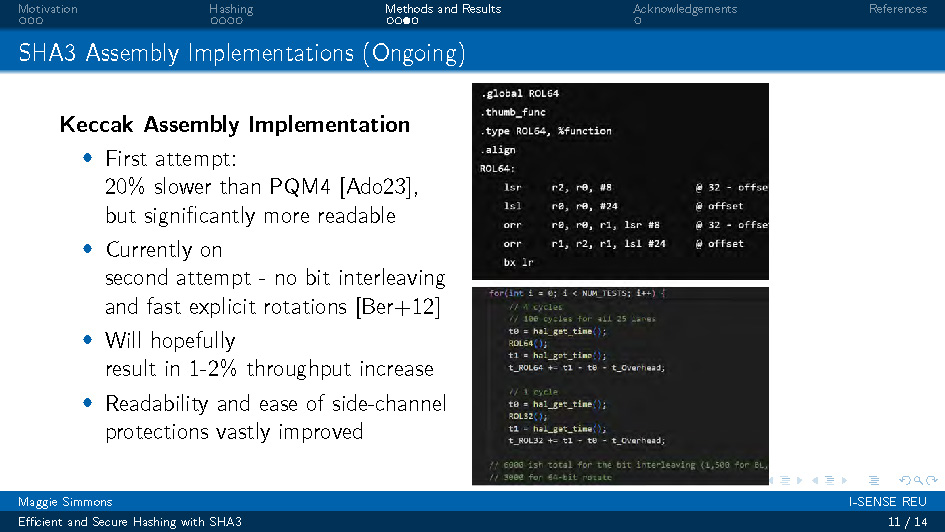
SHA3 Assembly Implementations (Ongoing)
Keccak Assembly Implementation
- First attempt: 20% slower than PQM4 [Ado23], but significantly more readable
- Currently on second attempt - no bit interleaving and fast explicit rotations [Ber+12]
- Will hopefully result in 1-2% throughput increase
- Readability and ease of side-channel protections vastly improved
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 11 / 14
Slide-12
Conclusion
Future Exploration
- Formal verification and side-channel analysis of new SHA3 implementation
- Exploration in performance increase in context of larger algorithms
- Optimization on the newly released ARM M52 Cortex
Conclusions
- PQC algorithms increasingly important due to advancements in quantum computers
- Small optimizations to key primitives like SHA3 have huge effect on PQC implementations
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 12 / 14
Slide-13
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the I-SENSE Program for making this summer experience possible. Special thanks to Dr. Reza, Maryam Taghi Zadeh, Merve Karabulut, and Daniel Owens for guiding me throughout the summer.
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 13 / 14

Slide-14
References
[PA11] G. Bertoni, J. Daemen, M. Peeters and G. Van Assche. The Keccak reference. Round 3 submission to NIST SHA-3. 2011. url: http://keccak.noekeon.org/Keccak-reference-3.0.pdf.
[Ber+12] Gianpiero Bertoni et al. Keccak Implementation Overview. Round 3 Report. SHA-3 Competition, Round 3. SHA-3 Competition, 2012.
[Div14] NIST Computer Security Division. SHA-3 Standard: Permutation-Based Hash and Extendable-Output Functions. FIPS Publication 202. National Institute of Standards and Technology, U.S. Department of Commerce, May 2014. url: http://csrc.nist.gov/publications/drafts/fips-202/fips_202_draft.pdf.
[Ado23] Alexandre Adomnicai. "An update on Keccak performance on ARMv7-M". In: Cryptology ePrint Archive (2023).
Maggie Simmons I-SENSE REU
Efficient and Secure Hashing with SHA3 14 / 14

End of Presentation
Click the right arrow to return to the beginning of the slide show.
For a downloadable version of this presentation, email: I-SENSE@FAU.