Detection of Alzheimer's Through Open Source Pose Estimation

Slide-1
Julia Horn and Brennen Farrell
Mentor: Dr. Behnaz Ghoraani & Mahmoud Seifallahi
FAU SUMMER I-SENSE REU (2023)
Slide-2
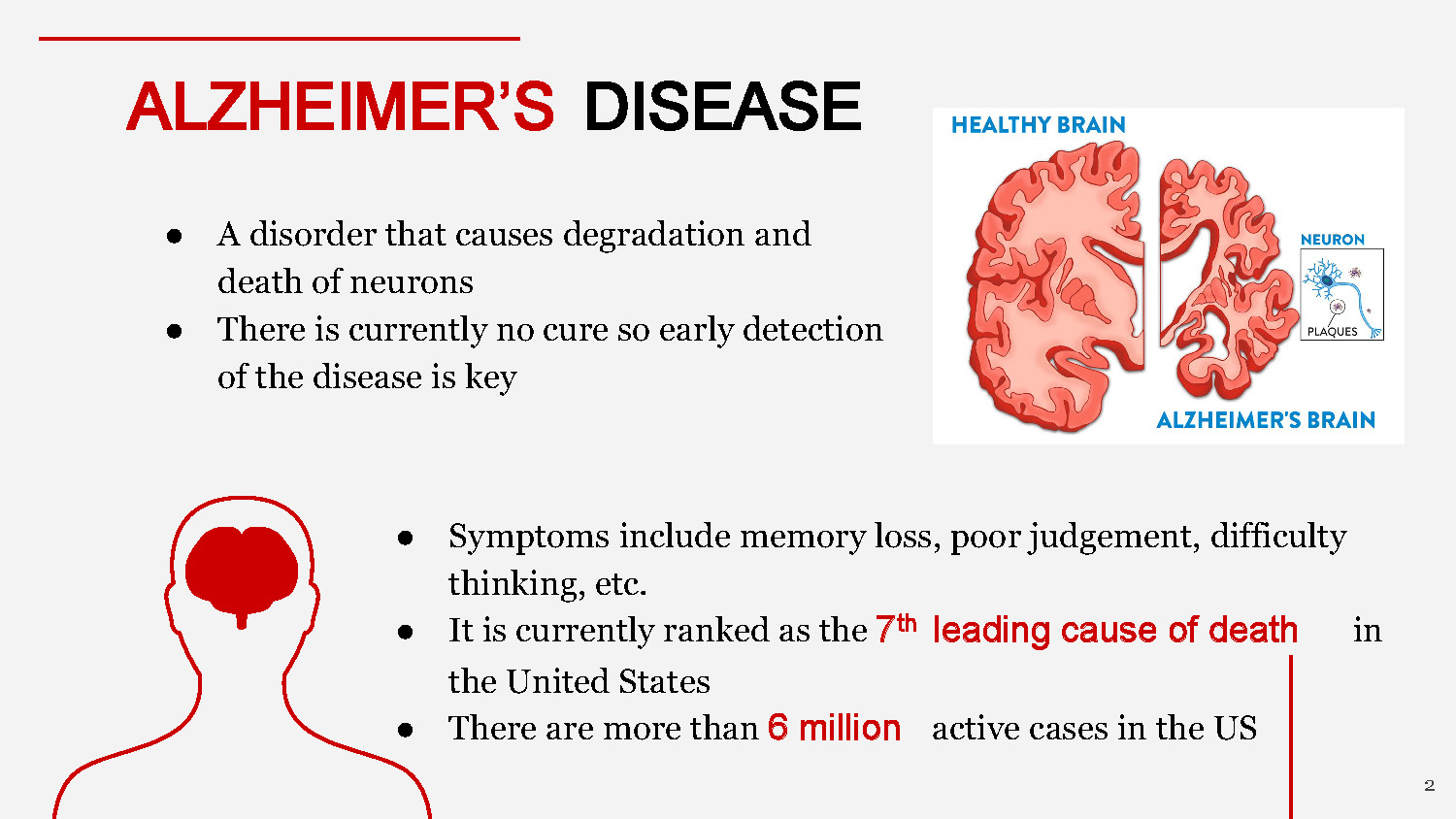
ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE
- A disorder that causes degradation and death of neurons
- There is currently no cure so early detection of the disease is key
- Symptoms include memory loss, poor judgement, difficulty thinking, etc.
- It is currently ranked as the 7th leading cause of death in the United States
- There are more than 6 million active cases in the US

Slide-3
OBJECTIVE
Our objective is to utilize pose estimation on visual content recorded on an ordinary camera to detect patterns of cognitive impairment in order to detect Alzheimer's disease.
- Studies have shown that certain factors of balance and gait are statistically different for individuals with Alzheimer's
- Ultimately, the application of this detection method could be used on an iPhone camera to make diagnosis of cognitive impairment accessible

Slide-4
INTRODUCTION
Pose Estimation
- Computer vision technique that identifies joint locations in visual content (images, videos, live webcams)
Popular Models (both for multi-person detection)
- AlphaPose
- Top-down method
- 1st : Detects and separates each person in an image.
- 2nd: Detects joints and connects them.
- Slower but can be more accurate
- OpenPose
- Bottom-up method
- 1st : Detects joints of the body.
- 2nd: Groups detected joints to form a person and pose.
- Quicker but may be less accurate

Slide-5
DEMO
This slide contains a demonstration of pose estimation technology, showing how the system detects and tracks human body joints and poses in real-time or from recorded video.
Slide-6
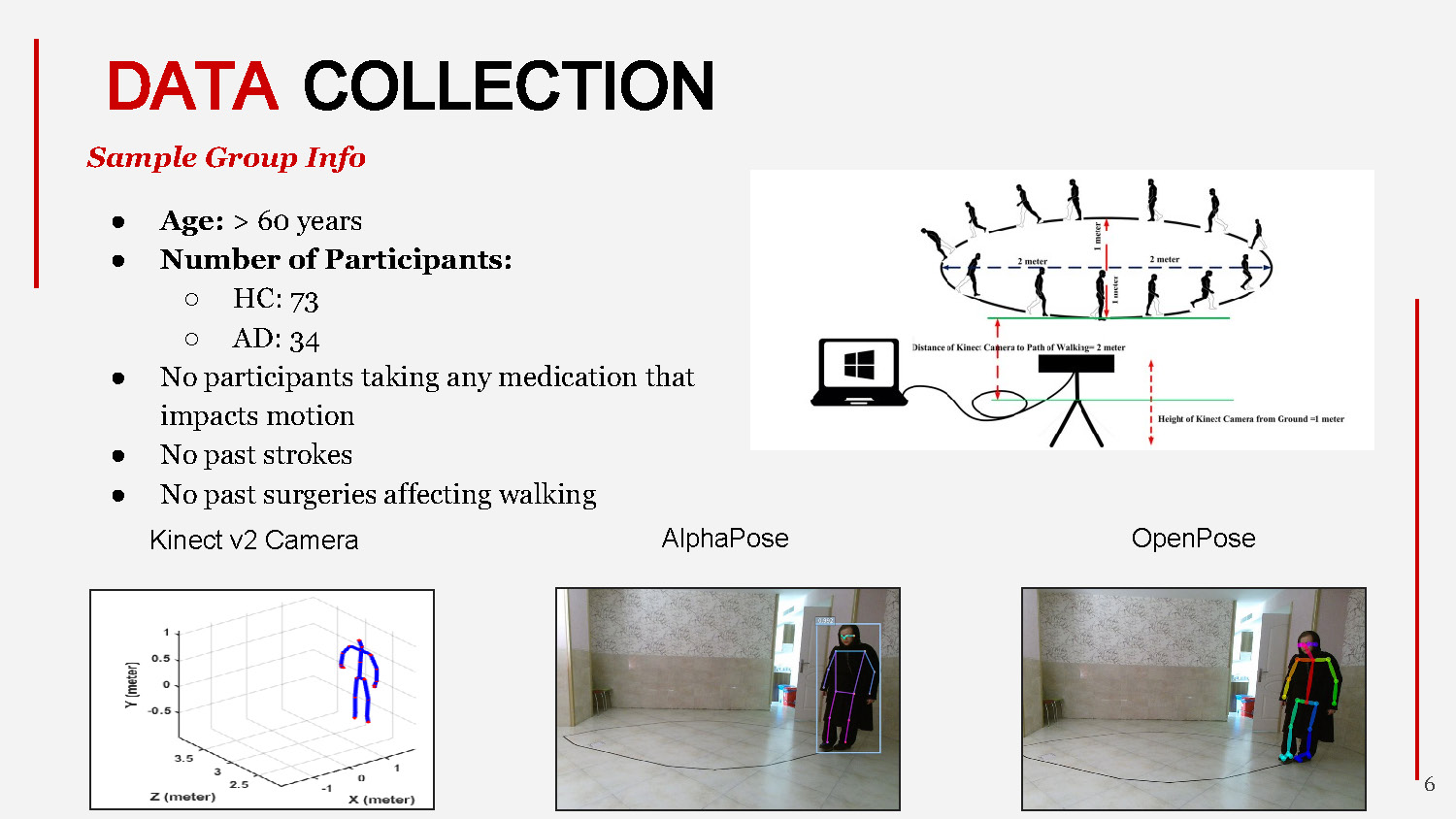
DATA COLLECTION
Sample Group Info
- Age: > 60 years
- Number of Participants:
- HC: 73
- AD: 34
- No participants taking any medication that impacts motion
- No past strokes
- No past surgeries affecting walking
Kinect v2 Camera
AlphaPose
OpenPose
Slide-7
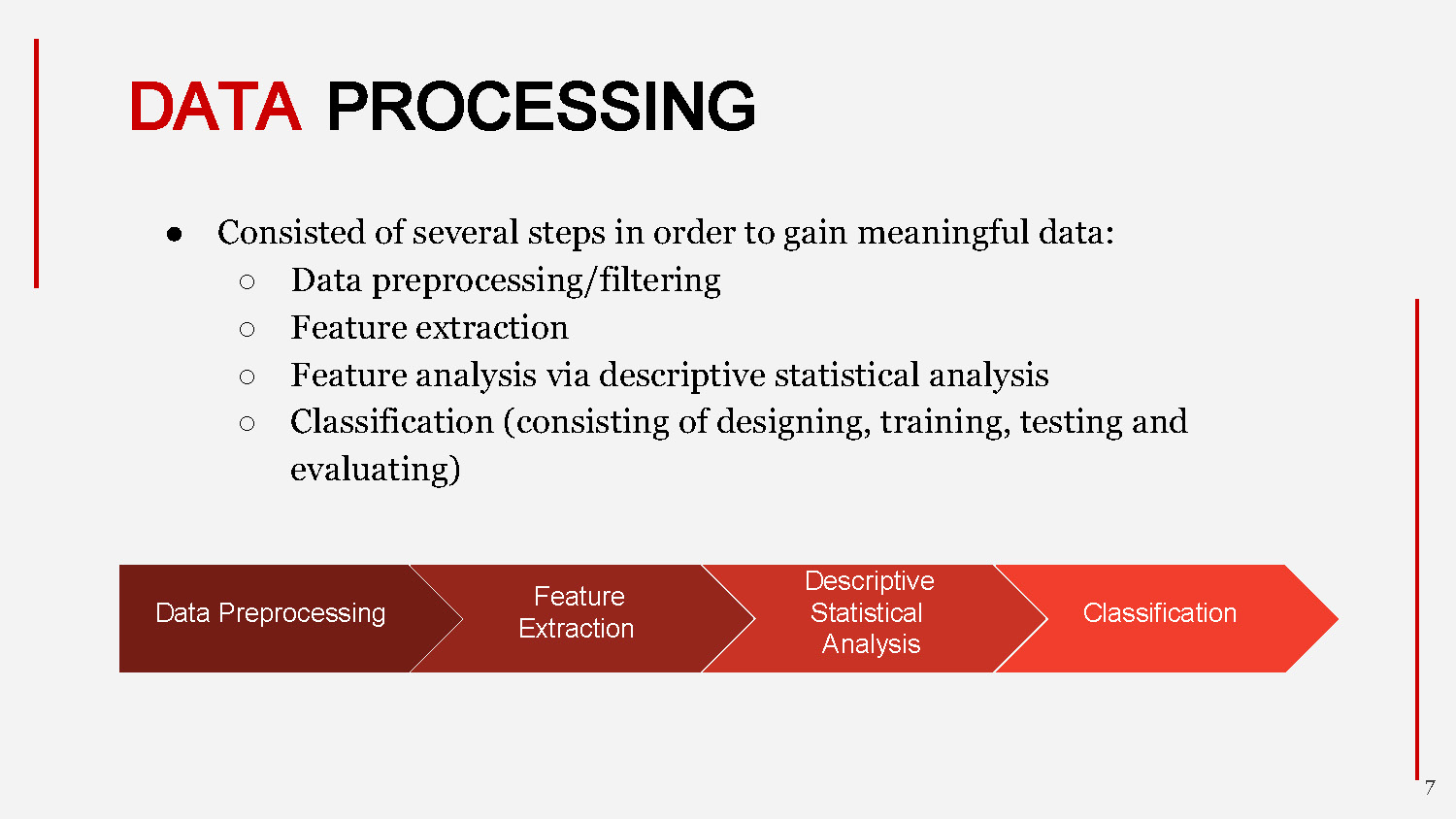
DATA PROCESSING
- Consisted of several steps in order to gain meaningful data:
- Data preprocessing/filtering
- Feature extraction
- Feature analysis via descriptive statistical analysis
- Classification (consisting of designing, training, testing and evaluating)
The workflow shows: Data Preprocessing → Feature Extraction → Descriptive Statistical Analysis → Classification

Slide-8
FEATURE EXTRACTION
Total features extracted: 48
- Macro Features: 6
- Walking Time, Gait Velocity, Step Number, Step Frequency, Stride Number, Stride Frequency
- Micro Features: 42
- These were collected as a mean, variability, and median of each feature below
- Stance Time, Swing Time, Double Support Time, Single Support Time, Step Length, Step Time, Step Velocity, Step Length Symmetry, Step Time Symmetry, Stride Time, Stride Length , Stride Velocity, Stride Length Regularity, Stride Time Regularity
Slide-9
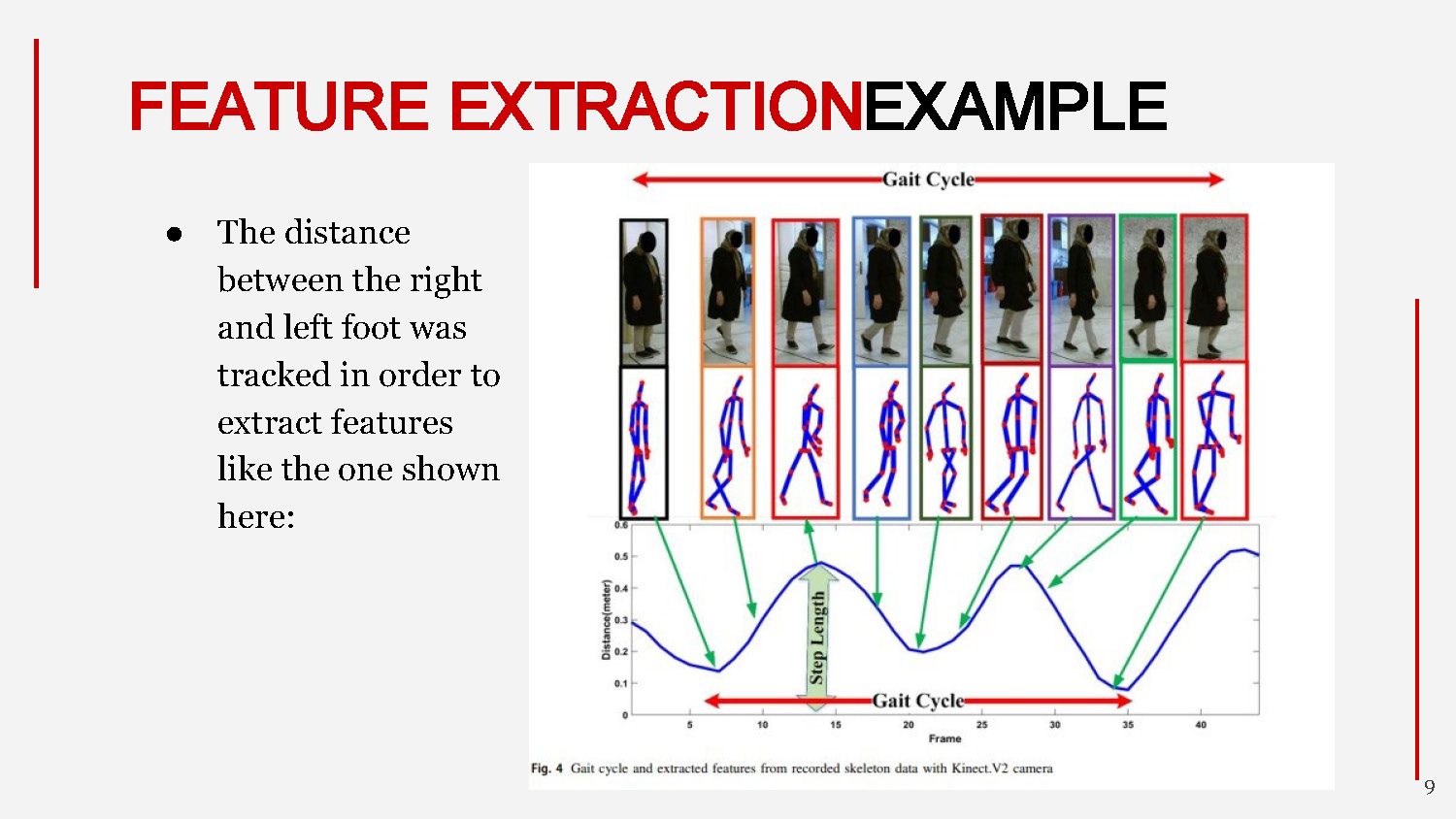
FEATURE EXTRACTION EXAMPLE
- The distance between the right and left foot was tracked in order to extract features like the one shown here:
The visualization shows how the system tracks the distance between feet over time to extract gait-related features.
Slide-10
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
- Feature significance was determined with the different parametric and nonparametric tests
Results:
- Only certain features showed a statistical significant difference between the groups (HC vs. AD)
- AlphaPose had the most significant features (41 features)
- There were 31 significant features in common between Kinect, AlphaPose, and OpenPose
Slide-11
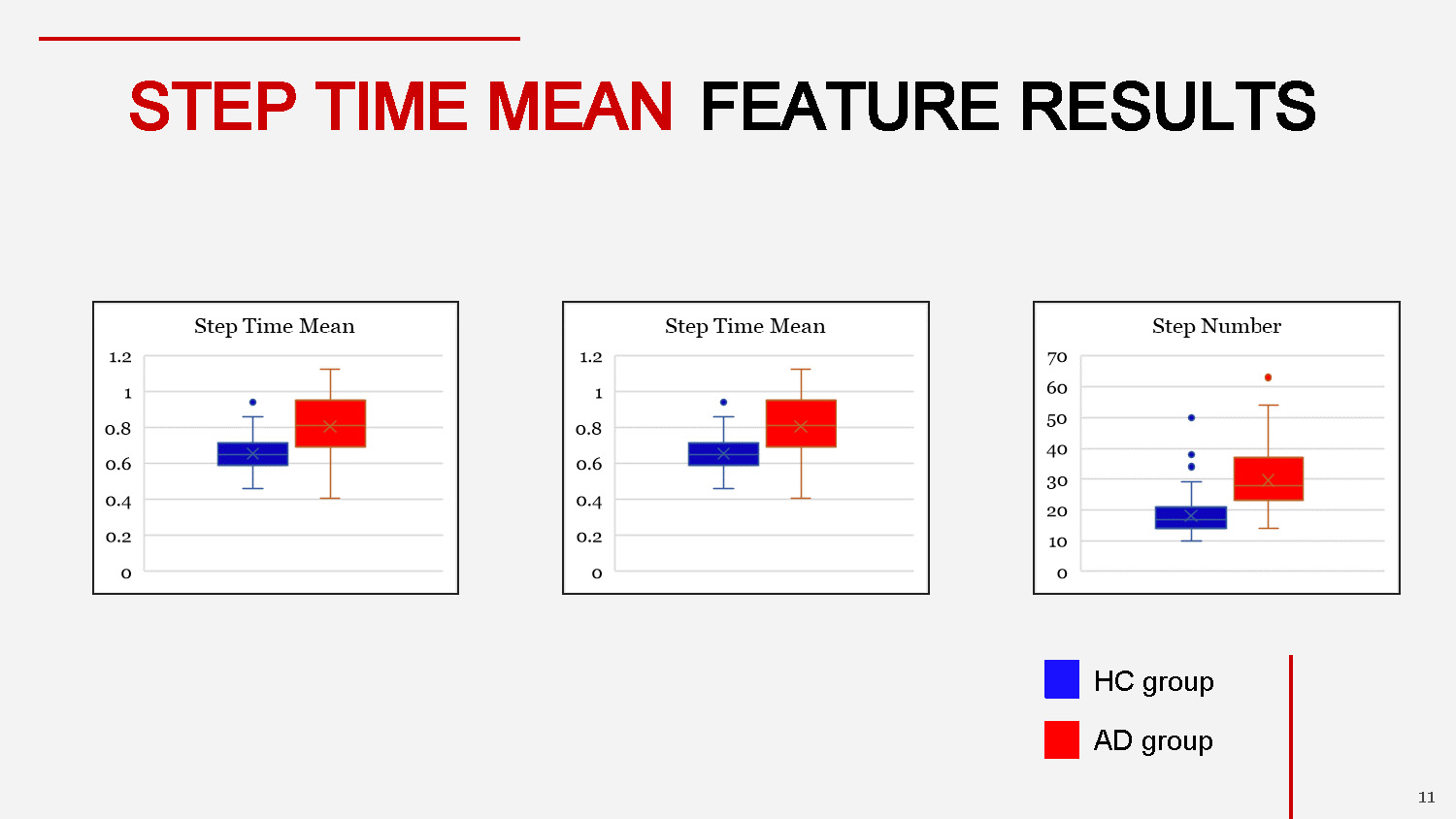
STEP TIME MEAN FEATURE RESULTS
This slide shows comparative graphs or visualizations of the step time mean feature between the Healthy Control (HC) group and the Alzheimer's Disease (AD) group, demonstrating the statistical differences in gait patterns.
Slide-12
DATA CLASSIFICATION
- Classifier: Support Vector Machine (SVM)
- "a supervised classification algorithm where we draw a line between two different categories to differentiate between them"
- K-Fold: 5
- "k-fold cross validation is a procedure used to estimate the skill of the model on new data"
- With k being = to 5, that means the given data is divided into 5 groups for training and testing
Slide-13
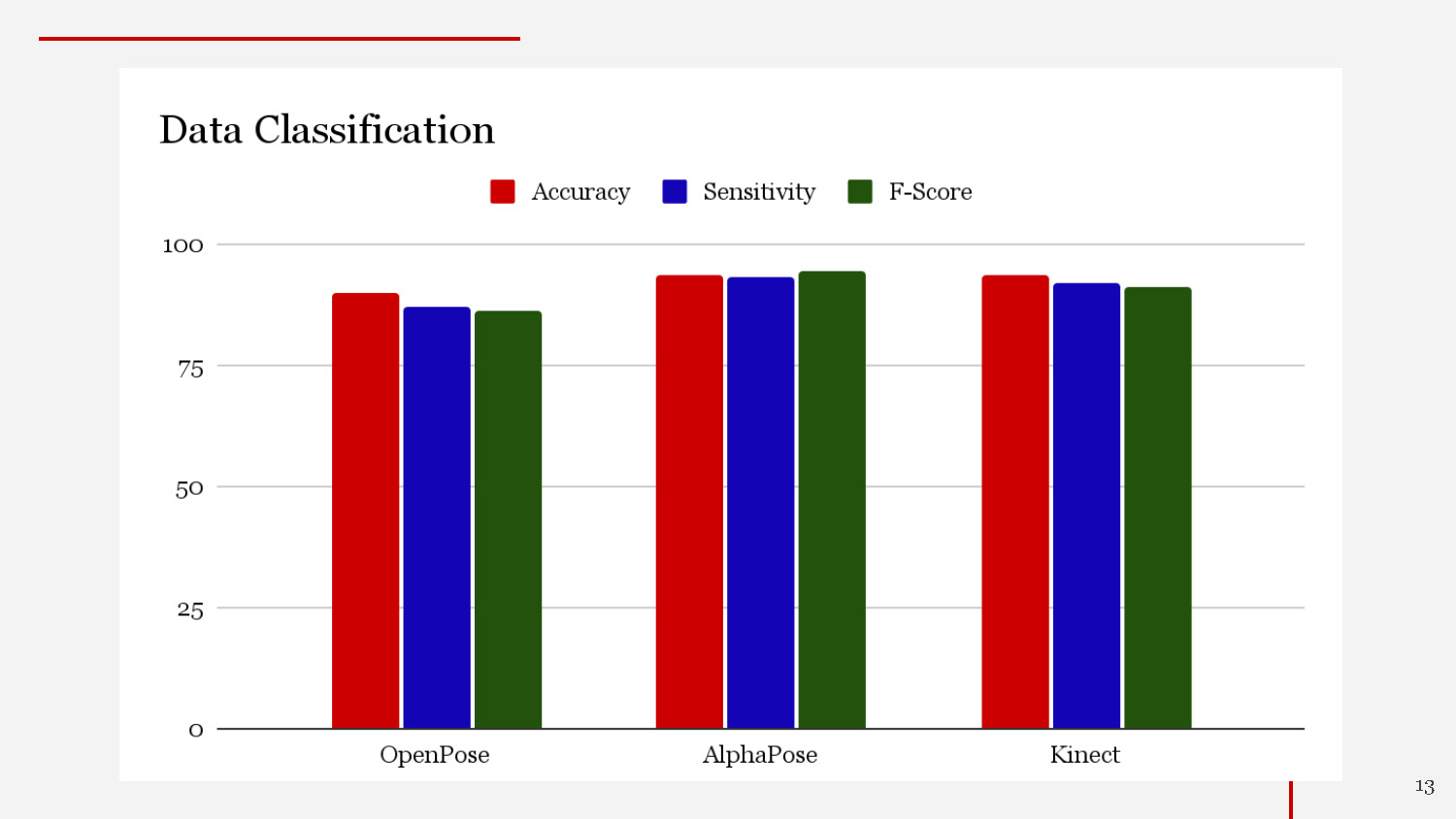
DATA CLASSIFICATION
The image is a bar chart titled "Data Classification." It compares three metrics—Accuracy (red), Sensitivity (blue), and F-Score (green)—across three categories: OpenPose, AlphaPose, and Kinect. Each category has three vertical bars, one for each metric. The y-axis ranges from 0 to 100 in increments of 25. The values for all metrics are between approximately 85 and 95. A legend above the chart identifies the colors of the three metrics.

Slide-14
CONCLUSION & FINDINGS
- Gait analysis of data recorded with a regular camera can be used instead of Kinect v2 Camera skeletal data to detect Alzheimer’s Disease and cognitive impairment
- Using signal processing and machine learning, these methods can effectively differentiate between a healthy and afflicted individual
- In comparing OpenPose and AlphaPose, AlphaPose demonstrated it was much better at detecting Alzheimer’s Disease as shown in the classification results.

End of Presentation
Click the right arrow to return to the beginning of the slide show.
For a downloadable version of this presentation, email: I-SENSE@FAU.