Domain Adaptation for Human Activity Recognition of Parkinson's Disease Patients

Slide-1
By: Maria Cardei
Mentor: Behnaz Ghoraani, Ph.D.
FAU I-SENSE REU Scholar 2022
Slide-2
Background
- Human activity recognition (HAR) uses machine learning to classify data acquired by wearable sensors into activities
- Parkinson's Disease (PD) diagnosis and prognosis can be improved with HAR
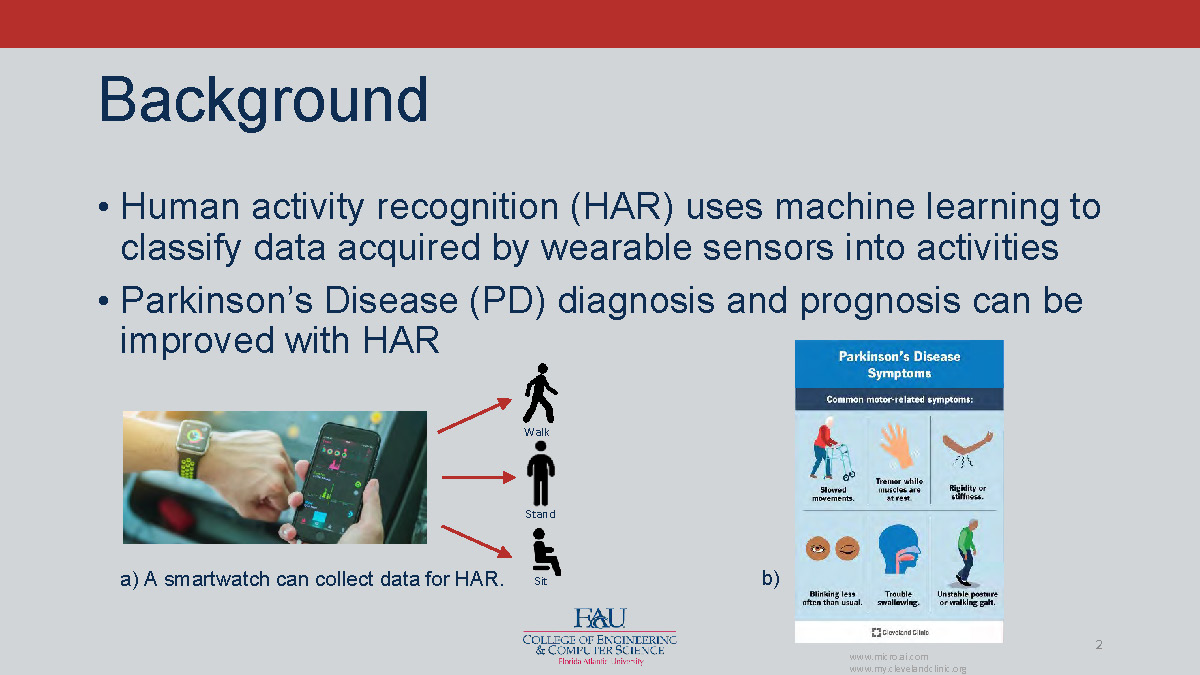
a) A smartwatch can collect data for HAR.
Activities shown: Walk, Stand, Sit
b) Poster of Parkinson's Disease Symptoms
Source references: www.micro.ai.com, www.my.clevelandclinic.org
Slide-3
HAR Challenges
- Various sensor types, placements on body, activity variability between people
- Minimal PD patient sensor data publicly available
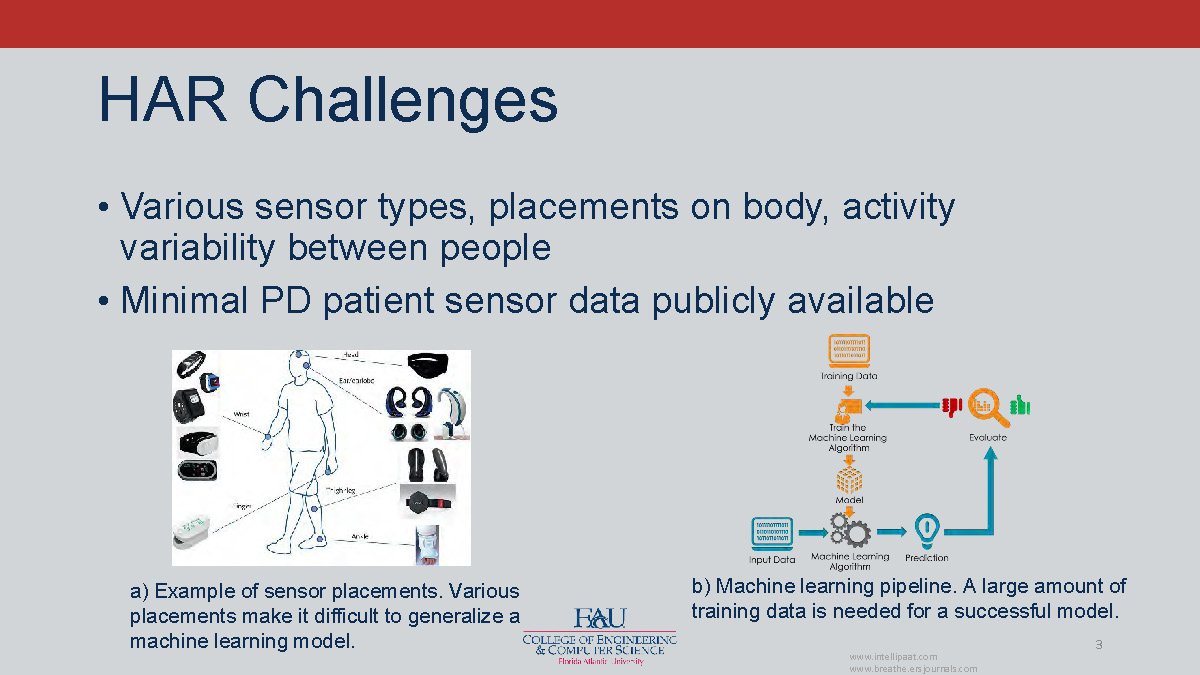
a) Example of sensor placements. Various placements make it difficult to generalize a machine learning model.
b) Machine learning pipeline. A large amount of training data is needed for a successful model.
Source references: www.intellipaat.com, www.breathe.ersjournals.com
Slide-4
Project Aim
Accurately classify the motion data of PD patients into activities of daily living using domain adaptation
Slide-5
Domain Adaptation (DA)
A way to address the domain shift between datasets
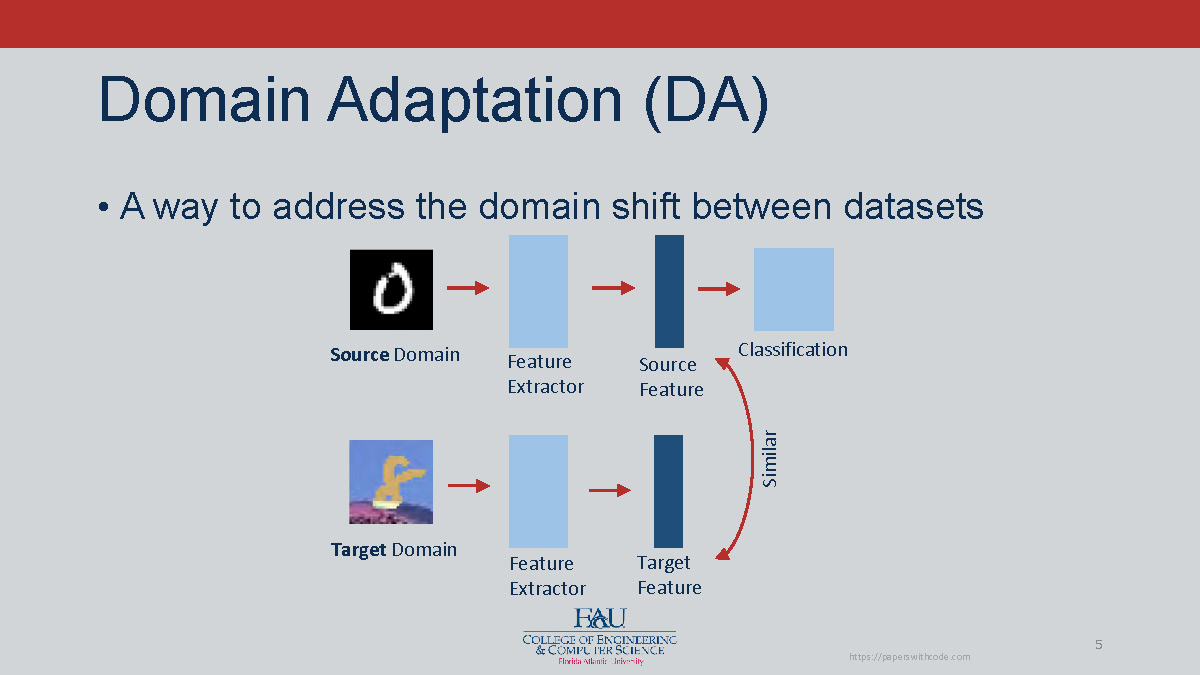
The diagram shows:
- Source Domain with Feature Extractor producing Source Feature
- Target Domain with Feature Extractor producing Target Feature
- Similar Classification between the domains
Source reference: https://paperswithcode.com
Slide-6
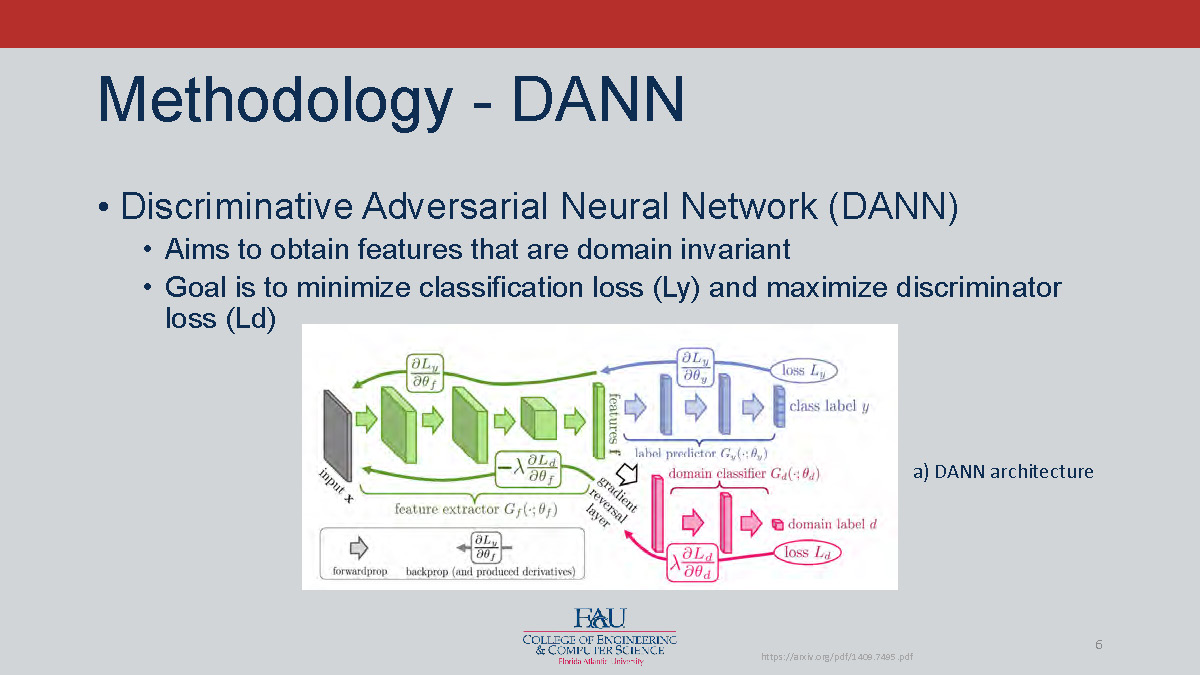
Methodology - DANN
- Discriminative Adversarial Neural Network (DANN)
- Aims to obtain features that are domain invariant
- Goal is to minimize classification loss (Ly) and maximize discriminator loss (Ld)
a) DANN architecture
Source reference: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.7495.pdf
Slide-7
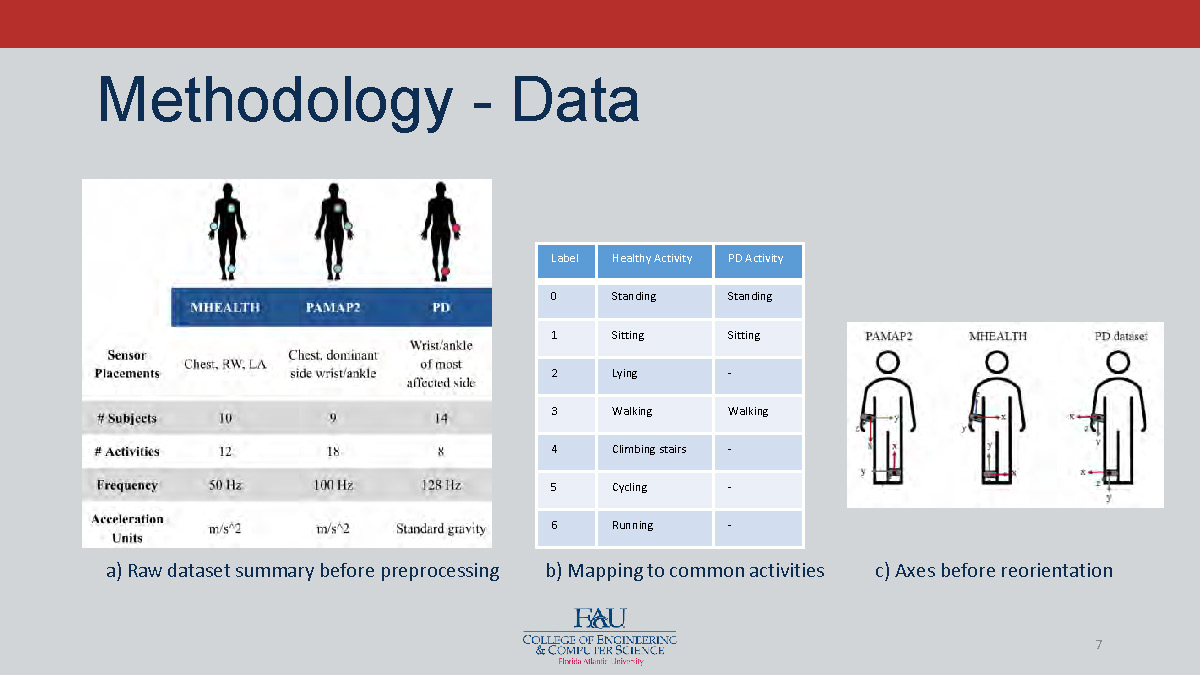
Methodology - Data
a) Raw dataset summary before preprocessing
b) Mapping to common activities
| Label | Healthy Activity | PD Activity |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Standing | Standing |
| 1 | Sitting | Sitting |
| 2 | Lying | - |
| 3 | Walking | Walking |
| 4 | Climbing stairs | - |
| 5 | Cycling | - |
| 6 | Running | - |
c) Axes before reorientation
Slide-8
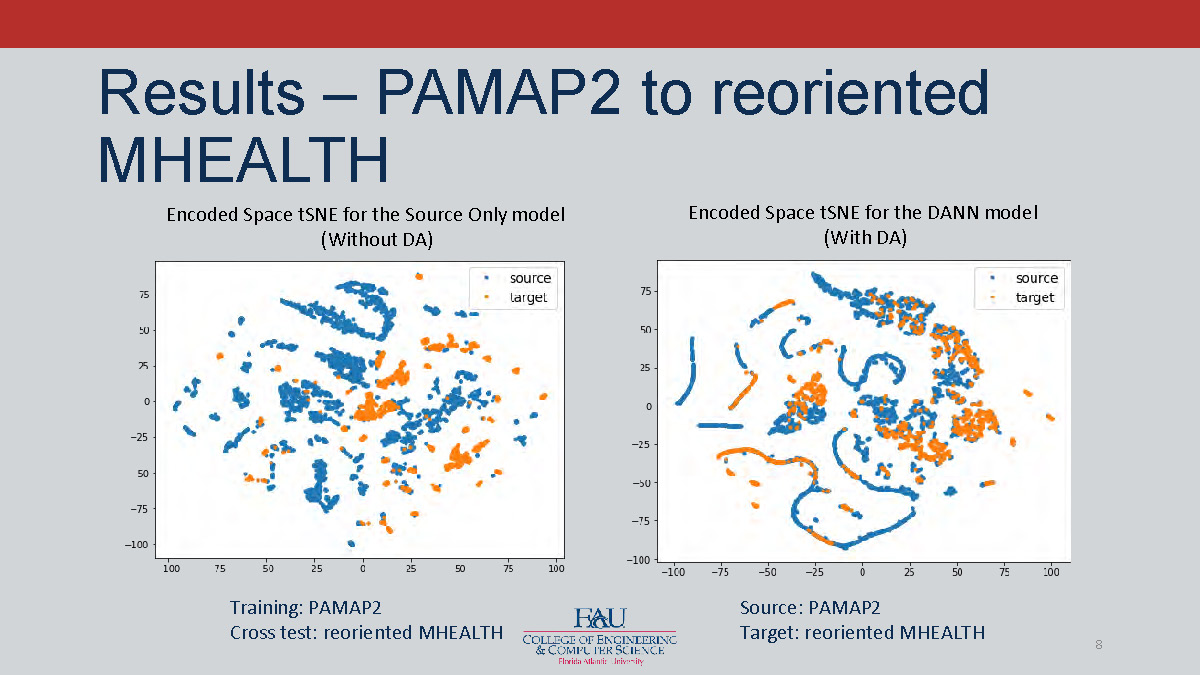
Results – PAMAP2 to reoriented MHEALTH
Encoded Space tSNE for the Source Only model (Without DA)
Training: PAMAP2 - scatter plot showing source and target
Cross test: reoriented MHEALTH
Source: PAMAP2- scatter plot showing source and target
Target: reoriented MHEALTH
Encoded Space tSNE for the DANN model (With DA)
Slide-9
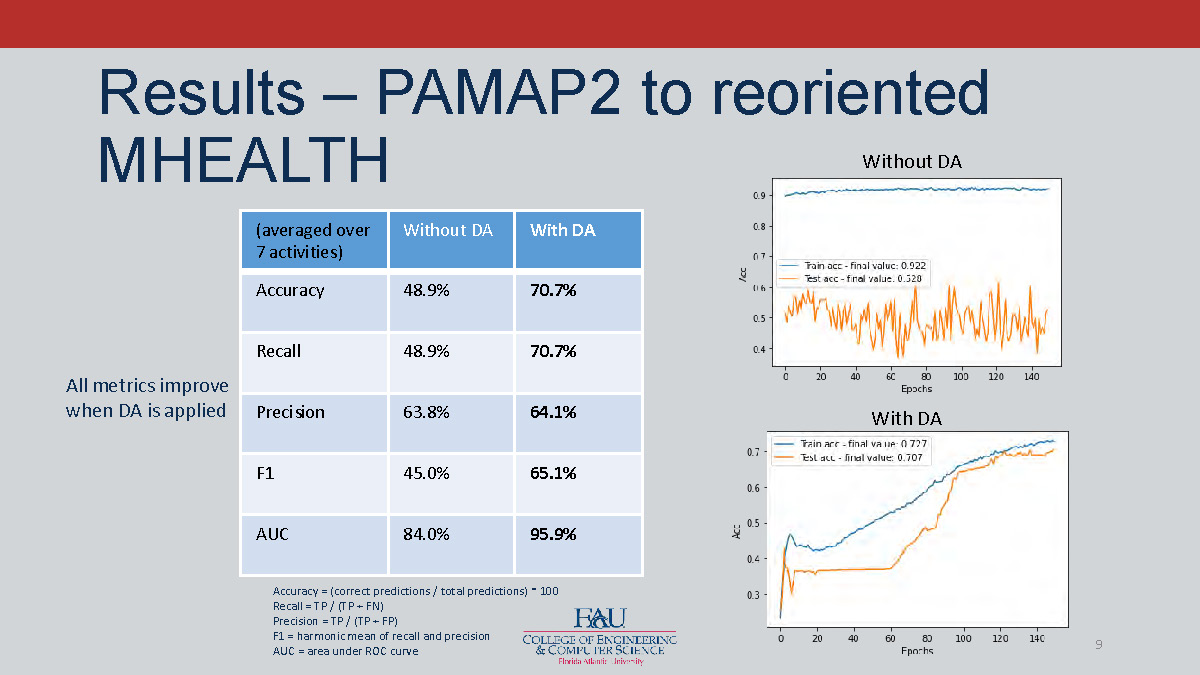
Results – PAMAP2 to reoriented MHEALTH
| (averaged over 7 activities) | Without DA | With DA |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 48.9% | 70.7% |
| Recall | 48.9% | 70.7% |
| Precision | 63.8% | 64.1% |
| F1 | 45.0% | 65.1% |
| AUC | 84.0% | 95.9% |
All metrics improve when DA is applied
Metric definitions:
- Accuracy = (correct predictions / total predictions) * 100
- Recall = TP / (TP + FN)
- Precision = TP / (TP + FP)
- F1 = harmonic mean of recall and precision
- AUC = area under ROC curve
Left: two graphs showing Without DA and With DA
Slide-10
Conclusions and Future Work
- DANN is a valuable DA method
- Data augmentation exploration
- Next step is to apply DANN to PD data
- Challenge of greater domain shift

Slide-11
Any questions? Thank you!

End of Presentation
Click the right arrow to return to the beginning of the slide show.
For a downloadable version of this presentation, email: I-SENSE@FAU.