Towards Efficient and Effective Smart Grid Control

Slide-1
Michael Aiudi
Ocean Engineering Student
University of Rhode Island Rising Senior
I-SENSE REU Final Presentation
08/04/17
Less CO2 emissions and a more reliably power system
Slide-2
Outline
- Background Information
- Method: PSO + Grid Search
- Simulation and Results
- Conclusion
Slide-3
Background of Smart Grid
What is a Smart grid
"… an electricity supply network that uses digital communications technology to detect and react to local changes in usage…"
Why do we need it
Decrease cost, waste, and response time:
- Easier add distributed generation and storage
- Coordination and Communication
- Detect errors
Slide-4
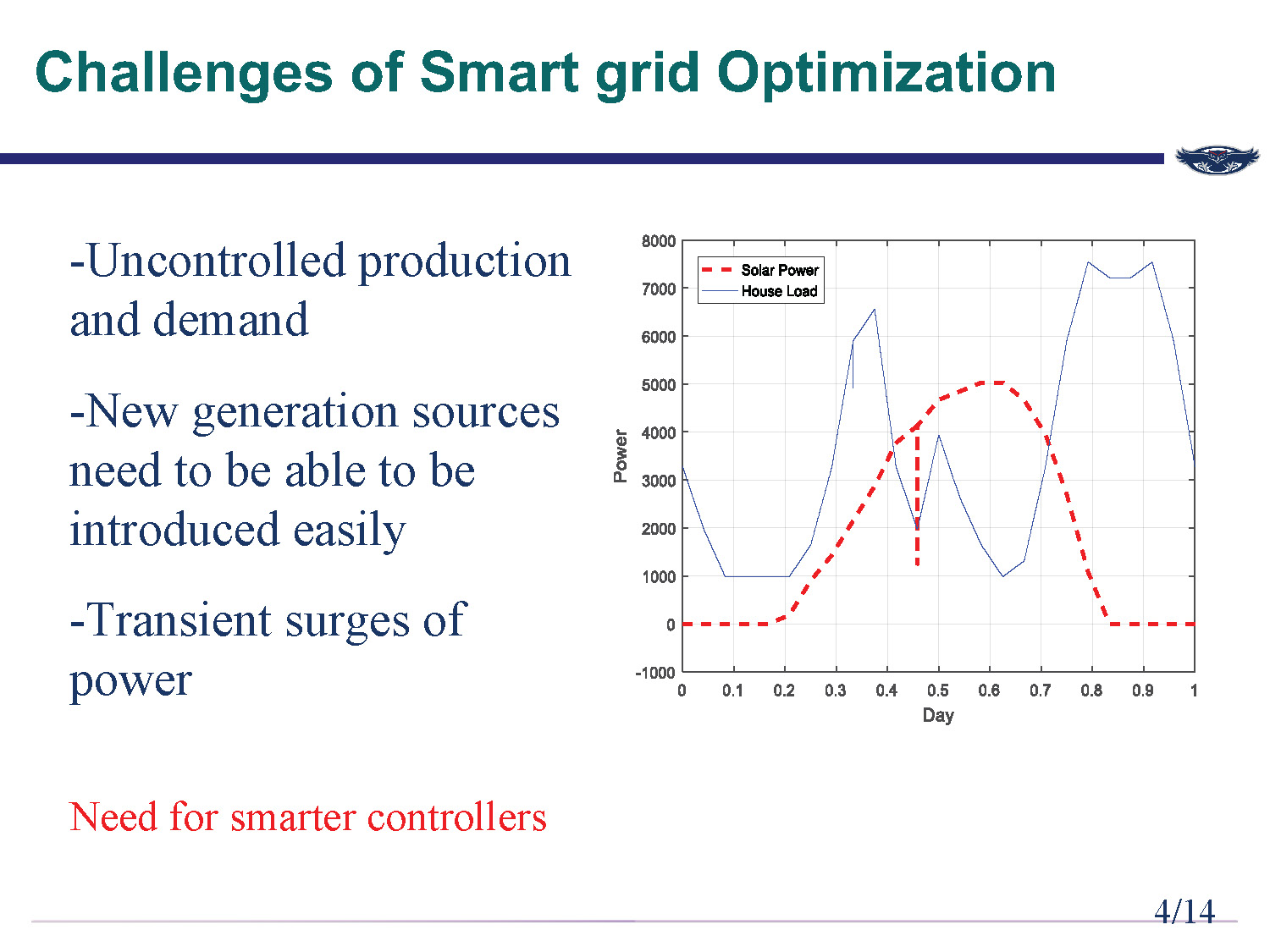
Challenges of Smart grid Optimization
- Uncontrolled production and demand
- New generation sources need to be able to be introduced easily
- Transient surges of power
Need for smarter controllers

Slide-5
What is: Particle Swarm Optimization
- A way of searching for an optimal point
- Originally based on a flock of birds
- Searches for best "food" location through communication
5/14
Slide-6
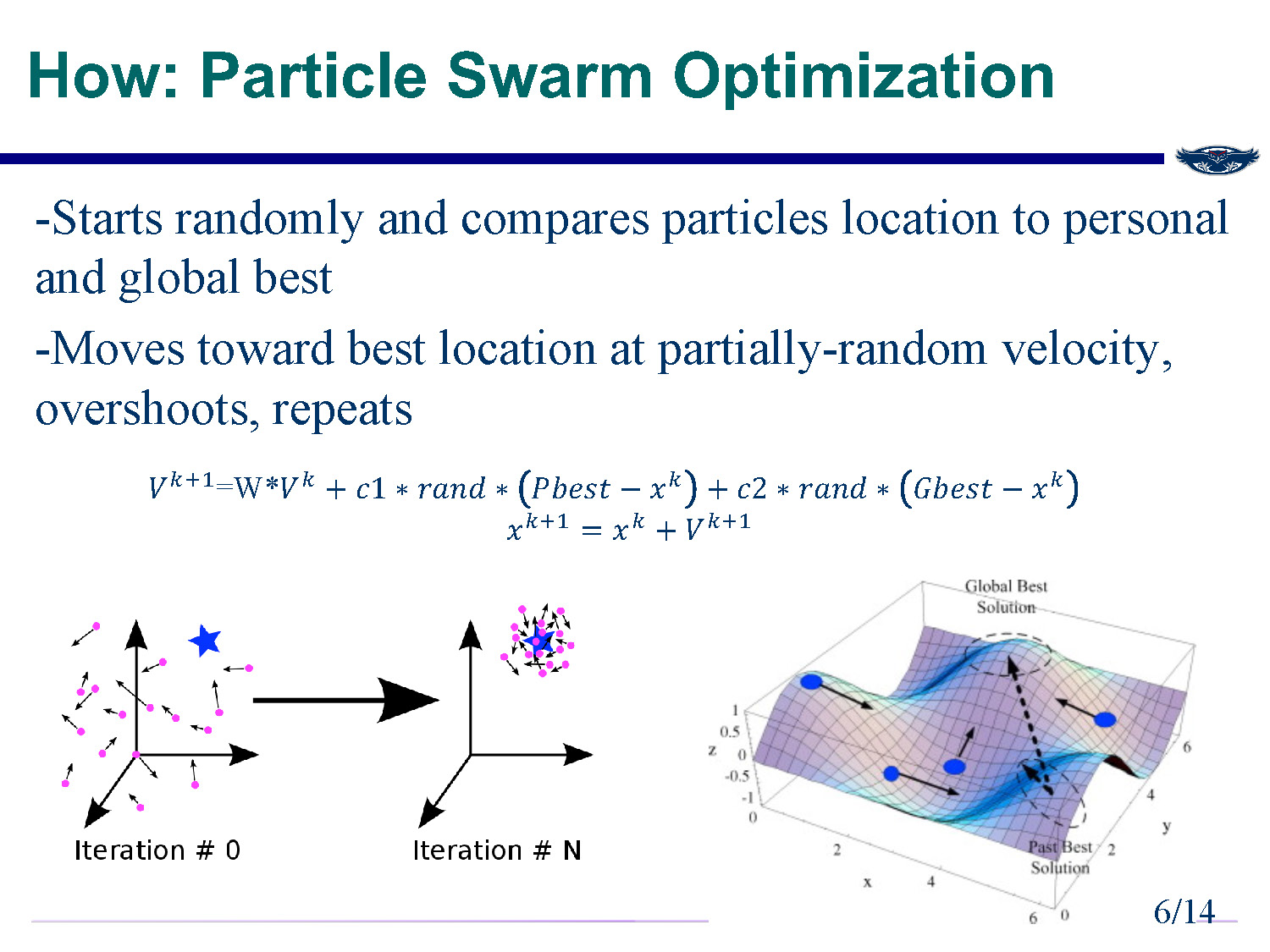
How: Particle Swarm Optimization
Starts randomly and compares particles location to personal and global best
Moves toward best location at partially-random velocity, overshoots, repeats
Vi t+1 = W*Vi t + c1 * rand * (Pbest - xi t) + c2 * rand * (Gbest - xi t)
xi t+1 = xi t + Vi t+1
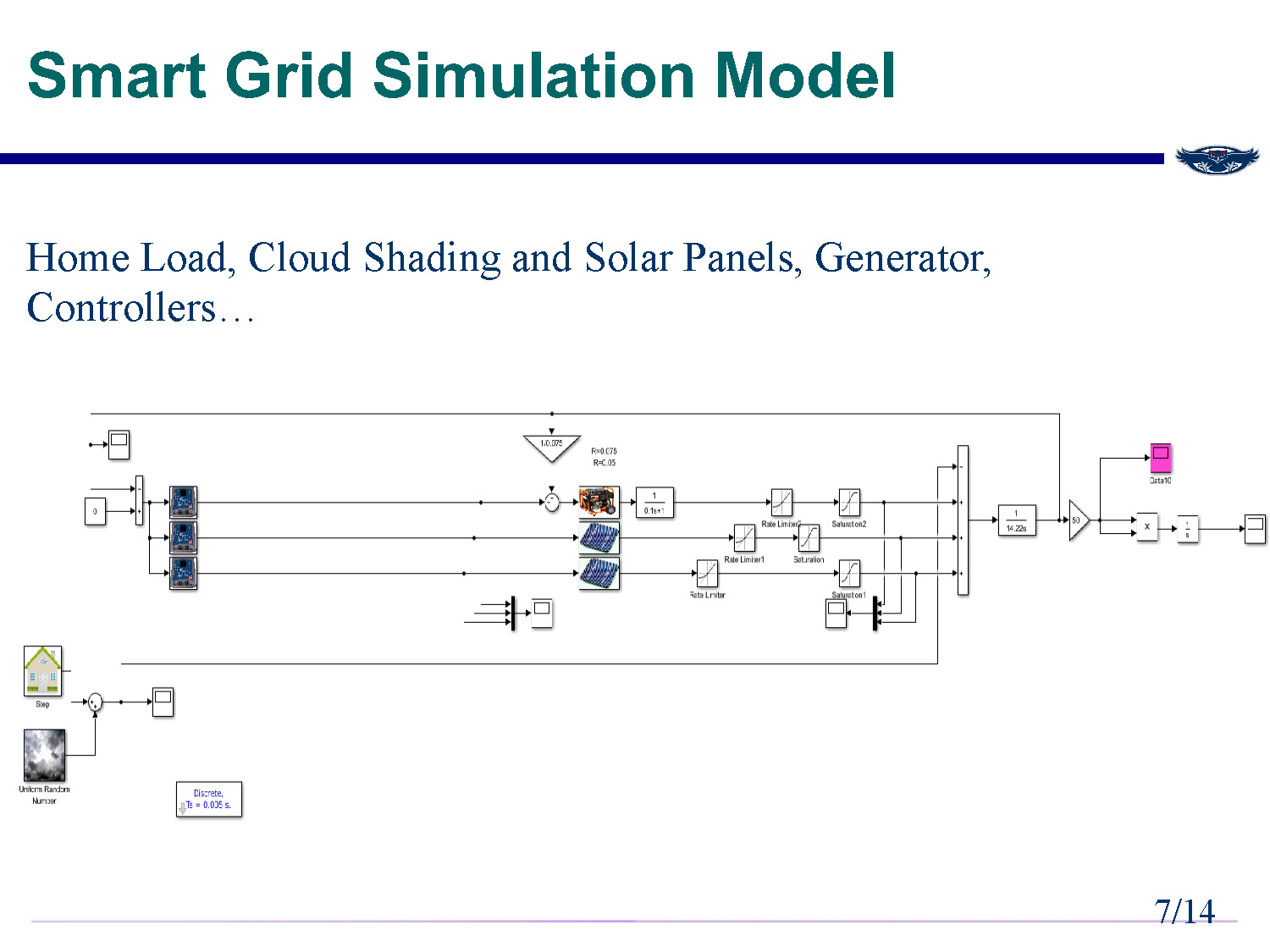
Slide-7
Smart Grid Simulation Model
Home Load, Cloud Shading and Solar Panels, Generator, Controllers…
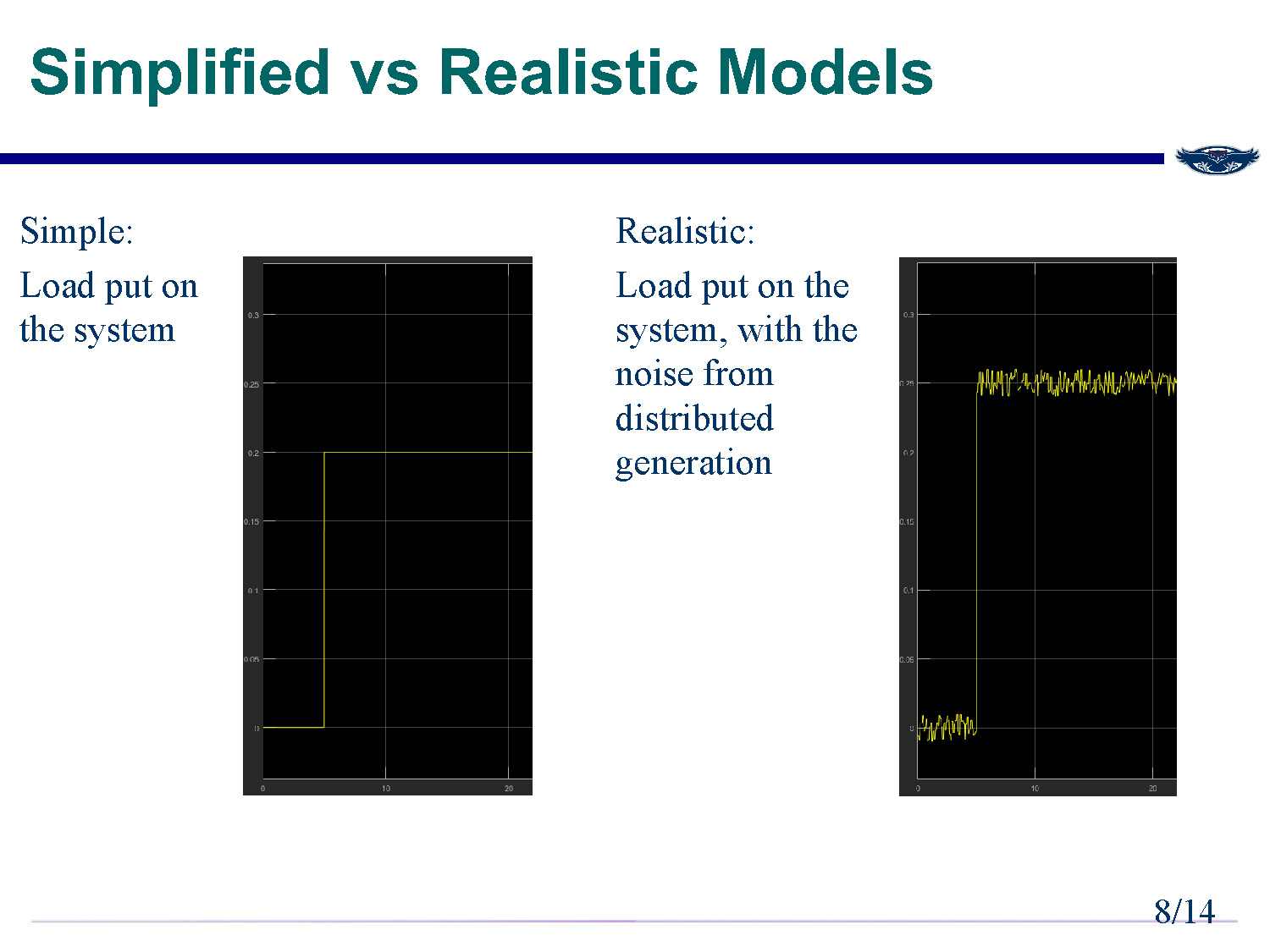
Slide-8
Simplified vs Realistic Models
Simple:
Load put on the system
Realistic:
Load put on the system, with the noise from distributed generation
Slide-9
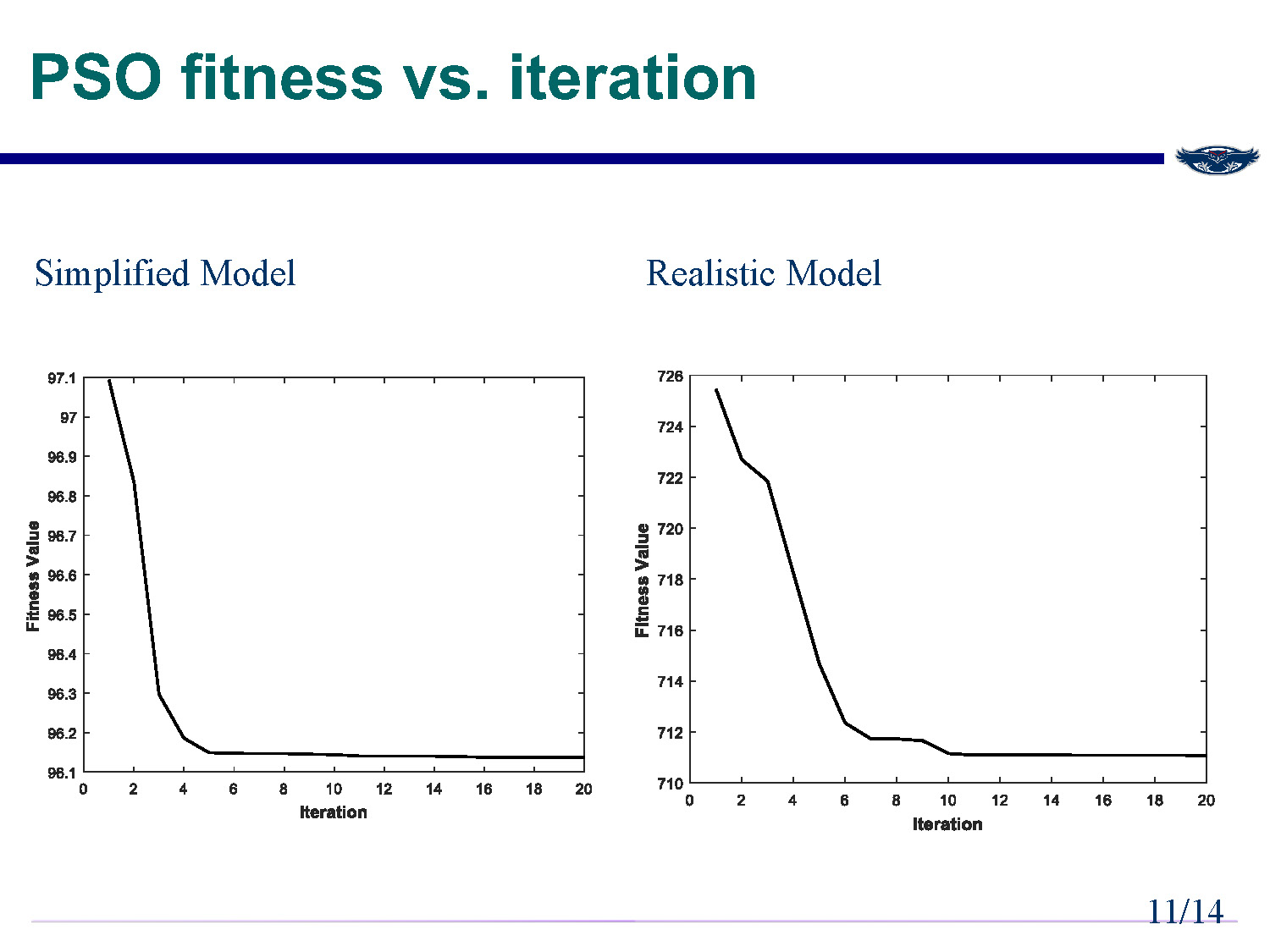
PSO fitness vs. iteration
Two graphs are shown comparing the fitness performance over iterations:
Simplified Model
Graph showing fitness improvement over iterations for the simplified model.
Realistic Model
Graph showing fitness improvement over iterations for the realistic model with distributed generation noise.
Slide-10
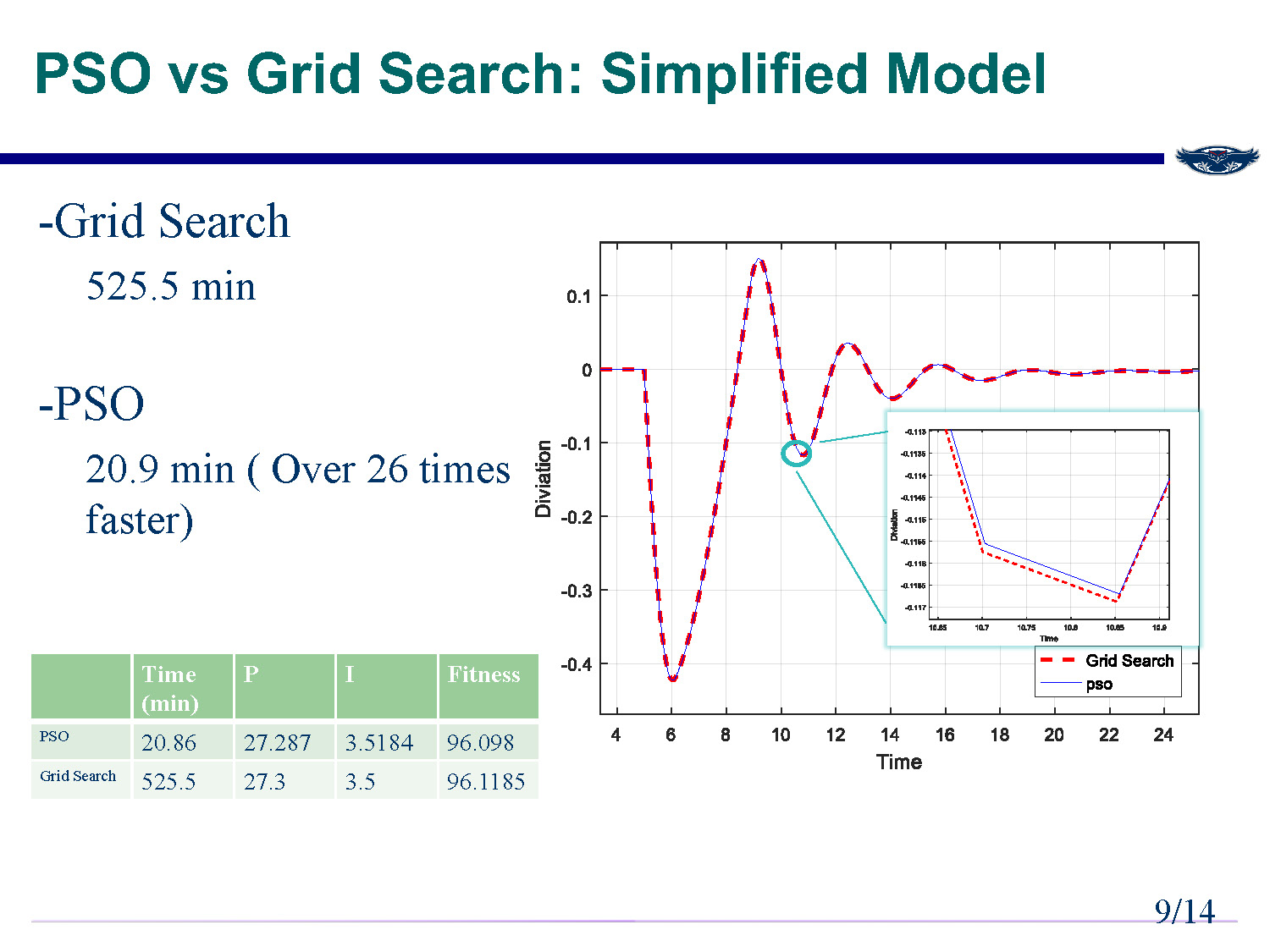
PSO vs Grid Search: Simplified Model
Grid Search: 525.5 min
PSO: 20.9 min (Over 26 times faster)
| Time (min) | P | I | Fitness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | 20.86 | 27.287 | 3.5184 | 96.098 |
| Grid Search | 525.5 | 27.3 | 3.5 | 96.1185 |
Slide-11
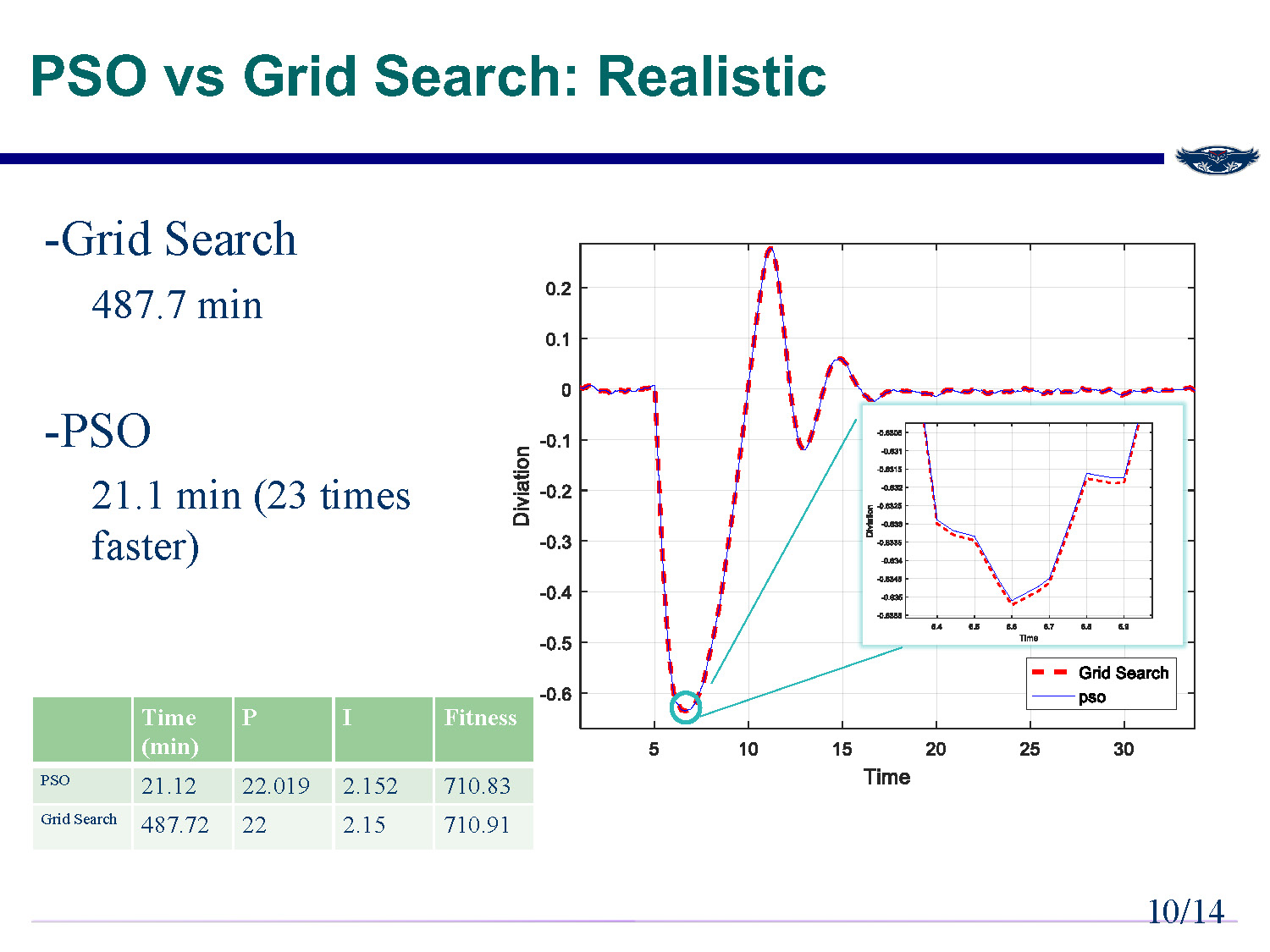
PSO vs Grid Search: Realistic
Grid Search: 487.7 min
PSO: 21.1 min (23 times faster)
| Time (min) | P | I | Fitness | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | 21.12 | 22.019 | 2.152 | 710.83 |
| Grid Search | 487.72 | 22 | 2.15 | 710.91 |

Slide-12
Conclusion
- Smart grid is the future of power systems
- It brings new challenges, such as frequency fluctuations
- Smart controllers can deal with these challenges through use of Particle Swarm Optimization

Slide-13
Acknowledgments
National Science Foundation
I-SENSE
Florida Atlantic University
Prof. Jason Hallstrom
Prof. Yufei Tang
Andrea Gonzalez and Mary Jo Jackson
The rest of the I-SENSE faculty, staff, and students

Slide-14
References
- http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/5762913/
- http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6563367/
- https://gradeup.co/p-pi-and-pid-controllers-i-ba51cc88-c453-11e5-8e45-0f580d23b1d8
- http://www.eesi.org/briefings/view/smart-grid-how-does-it-work-and-why-do-we-need-it
- http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=488968
- https://www.google.com/search?q=florida+atlantic+university&rlz=1C1GGRV_enUS751US751&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiMtLHSz7PVAhWCRCYKHVccCoYQ_AUIDCgD&biw=1920&bih=974#imgrc=LQqdZKYOMzkkWM
- https://www.google.com/search?q=university+of+rhode+island&rlz=1C1GGRV_enUS751US751&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjW1IuP0LPVAhXK5yYKHZdiA8EQ_AUICygC&biw=1920&bih=974#imgrc=5SKso2reApAgzM
- https://www.google.com/search?q=smartgrid&rlz=1C1GGRV_enUS751US751&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwio-oya8bbVAhUGySYKHe6mBNUQ_AUICygC&biw=1745&bih=885#imgrc=eW24-XM-cGXDzM
- https://www.google.com/search?q=what+is+a+smart+grid&rlz=1C1GGRV_enUS751US751&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjx6ruk6LbVAhVBRyYKHboVDUwQ_AUIDCgD&biw=1745&bih=885#imgrc=Hfl--1BE1afn4M
- https://www.google.com/search?q=pso+birds&rlz=1C1GGRV_enUS751US751&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiUzoK57vTUAhUFNT4KHekyALkQ_AUICygC&biw=1920&bih=925#tbm=isch&q=bird+flock+and+school+of+fish&imgrc=goppaTBw5hs8iM
- https://www.google.com/search?q=particle+swarm+optimization&rlz=1C1GGRV_enUS751US751&tbm=isch&source=lnms&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiYieWm7fTUAhUPET4KHWnZDn4Q_AUICCgD&biw=1920&bih=925#imgrc=uRrIlg0-kR7srM
- https://www.google.com/search?q=particle+swarm+optimization&rlz=1C1GGRV_enUS751US751&tbm=isch&source=lnms&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiYieWm7fTUAhUPET4KHWnZDn4Q_AUICCgD&biw=1920&bih=974#imgrc=kCRSZSu86QgB9M
- https://www.google.com/search?rlz=1C1GGRV_enUS751US751&biw=1745&bih=841&tbm=isch&sa=1&q=I+SENSE+fau&oq=I+SENSE+fau&gs_l=psy-ab.3...5042.6577.0.6992.4.4.0.0.0.0.66.233.4.4.0....0...1.1.64.psy-ab..0.2.118...0j0i8i30k1.yCAolKklOoY#imgrc=bWcbSAuAaaEVDM

End of Presentation
Click the right arrow to return to the beginning of the slide show.
For a downloadable version of this presentation, email: I-SENSE@FAU.